Tissue phosphoproteomics with PolyMAC identifies potential therapeutic targets in a transgenic mouse model of HER2 positive breast cancer
- PMID: 24723360
- PMCID: PMC4193948
- DOI: 10.1002/elps.201400022
Tissue phosphoproteomics with PolyMAC identifies potential therapeutic targets in a transgenic mouse model of HER2 positive breast cancer
Abstract
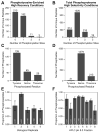
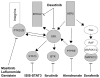
Altered protein phosphorylation is a feature of many human cancers that can be targeted therapeutically. Phosphopeptide enrichment is a critical step for maximizing the depth of phosphoproteome coverage by MS, but remains challenging for tissue specimens because of their high complexity. We describe the first analysis of a tissue phosphoproteome using polymer-based metal ion affinity capture (PolyMAC), a nanopolymer that has excellent yield and specificity for phosphopeptide enrichment, on a transgenic mouse model of HER2-driven breast cancer. By combining phosphotyrosine immunoprecipitation with PolyMAC, 411 unique peptides with 139 phosphotyrosine, 45 phosphoserine, and 29 phosphothreonine sites were identified from five LC-MS/MS runs. Combining reverse phase liquid chromatography fractionation at pH 8.0 with PolyMAC identified 1571 unique peptides with 1279 phosphoserine, 213 phosphothreonine, and 21 phosphotyrosine sites from eight LC-MS/MS runs. Linear motif analysis indicated that many of the phosphosites correspond to well-known phosphorylation motifs. Analysis of the tyrosine phosphoproteome with the Drug Gene Interaction database uncovered a network of potential therapeutic targets centered on Src family kinases with inhibitors that are either FDA-approved or in clinical development. These results demonstrate that PolyMAC is well suited for phosphoproteomic analysis of tissue specimens.
Keywords: Breast Cancer; Drug identification; HER2; Phosphoproteomics; PolyMAC.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
A.C.S., T.S.C, L.A.C, and R.B. declare no conflicts of interest. A.B.I. and W.A.T. are principals at Tymora Analytical Operations LLC, the company which currently sells PolyMAC-Ti and was formed after the research in this manuscript was conducted.
Figures

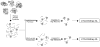

Similar articles
-
Functionalized soluble nanopolymers for phosphoproteome analysis.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;790:277-85. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-319-6_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21948422
-
High-Throughput Characterization of Histidine Phosphorylation Sites Using UPAX and Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2077:225-235. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9884-5_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31707662
-
In-Depth Analyses of B Cell Signaling Through Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Phosphopeptides Enriched by PolyMAC.Int J Mass Spectrom. 2015 Feb 1;377:744-753. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2014.08.032. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2015. PMID: 25954137 Free PMC article.
-
Off-line high-pH reversed-phase fractionation for in-depth phosphoproteomics.J Proteome Res. 2014 Dec 5;13(12):6176-86. doi: 10.1021/pr500893m. Epub 2014 Nov 4. J Proteome Res. 2014. PMID: 25338131
-
[Advances in the methods of phosphopeptide enrichment and separation in phosphoproteomic research].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022 Oct 25;38(10):3648-3658. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.220599. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 36305400 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Comparing multistep immobilized metal affinity chromatography and multistep TiO2 methods for phosphopeptide enrichment.Anal Chem. 2015 Sep 1;87(17):8837-44. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01833. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 26237447 Free PMC article.
-
Recent findings and technological advances in phosphoproteomics for cells and tissues.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2015;12(5):469-87. doi: 10.1586/14789450.2015.1078730. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 26400465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoproteomics in the Age of Rapid and Deep Proteome Profiling.Anal Chem. 2016 Jan 5;88(1):74-94. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04123. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Anal Chem. 2016. PMID: 26539879 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Recent advances in phosphoproteomics and application to neurological diseases.Analyst. 2017 Nov 20;142(23):4373-4387. doi: 10.1039/c7an00985b. Analyst. 2017. PMID: 29094114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating proteomics with electrochemistry for identifying kinase biomarkers.Chem Sci. 2015 Aug 1;6(8):4756-4766. doi: 10.1039/c5sc00560d. Epub 2015 May 22. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 29142712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2408–2417. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Geyer CE, Forster J, Lindquist D, Chan S, Romieu CG, Pienkowski T. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2733–2743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

