Tissue phosphoproteomics with PolyMAC identifies potential therapeutic targets in a transgenic mouse model of HER2 positive breast cancer
- PMID: 24723360
- PMCID: PMC4193948
- DOI: 10.1002/elps.201400022
Tissue phosphoproteomics with PolyMAC identifies potential therapeutic targets in a transgenic mouse model of HER2 positive breast cancer
Abstract
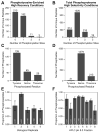
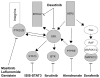
Altered protein phosphorylation is a feature of many human cancers that can be targeted therapeutically. Phosphopeptide enrichment is a critical step for maximizing the depth of phosphoproteome coverage by MS, but remains challenging for tissue specimens because of their high complexity. We describe the first analysis of a tissue phosphoproteome using polymer-based metal ion affinity capture (PolyMAC), a nanopolymer that has excellent yield and specificity for phosphopeptide enrichment, on a transgenic mouse model of HER2-driven breast cancer. By combining phosphotyrosine immunoprecipitation with PolyMAC, 411 unique peptides with 139 phosphotyrosine, 45 phosphoserine, and 29 phosphothreonine sites were identified from five LC-MS/MS runs. Combining reverse phase liquid chromatography fractionation at pH 8.0 with PolyMAC identified 1571 unique peptides with 1279 phosphoserine, 213 phosphothreonine, and 21 phosphotyrosine sites from eight LC-MS/MS runs. Linear motif analysis indicated that many of the phosphosites correspond to well-known phosphorylation motifs. Analysis of the tyrosine phosphoproteome with the Drug Gene Interaction database uncovered a network of potential therapeutic targets centered on Src family kinases with inhibitors that are either FDA-approved or in clinical development. These results demonstrate that PolyMAC is well suited for phosphoproteomic analysis of tissue specimens.
Keywords: Breast Cancer; Drug identification; HER2; Phosphoproteomics; PolyMAC.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
A.C.S., T.S.C, L.A.C, and R.B. declare no conflicts of interest. A.B.I. and W.A.T. are principals at Tymora Analytical Operations LLC, the company which currently sells PolyMAC-Ti and was formed after the research in this manuscript was conducted.
Figures

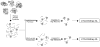

References
-
- Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2408–2417. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S. Science. 2004;304:1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–2139. - PubMed
-
- Geyer CE, Forster J, Lindquist D, Chan S, Romieu CG, Pienkowski T. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2733–2743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

