Micro-masters of glioblastoma biology and therapy: increasingly recognized roles for microRNAs
- PMID: 24723563
- PMCID: PMC3984565
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nou049
Micro-masters of glioblastoma biology and therapy: increasingly recognized roles for microRNAs
Abstract
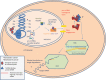
MicroRNAs are small noncoding RNAs encoded in eukaryotic genomes that have been found to play critical roles in most biological processes, including cancer. This is true for glioblastoma, the most common and lethal primary brain tumor, for which microRNAs have been shown to strongly influence cell viability, stem cell characteristics, invasiveness, angiogenesis, metabolism, and immune evasion. Developing microRNAs as prognostic markers or as therapeutic agents is showing increasing promise and has potential to reach the clinic in the next several years. This succinct review summarizes current progress and future directions in this exciting and steadily expanding field.
Keywords: glioblastoma; microRNA; review.
Figures
References
-
- Gregory RI, Yan KP, Amuthan G, et al. The microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature. 2004;432(7014):235–240. - PubMed
-
- Sen GL, Blau HM. Argonaute 2/RISC resides in sites of mammalian mRNA decay known as cytoplasmic bodies. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7(6):633–636. - PubMed
-
- Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, et al. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17–92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005;65(21):9628–9632. - PubMed
-
- Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, et al. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell. 2005;120(5):635–647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical