Membrane lipids in Agrobacterium tumefaciens: biosynthetic pathways and importance for pathogenesis
- PMID: 24723930
- PMCID: PMC3972451
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00109
Membrane lipids in Agrobacterium tumefaciens: biosynthetic pathways and importance for pathogenesis
Abstract
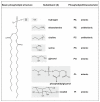
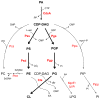
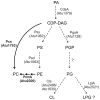
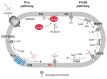
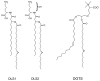
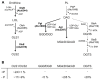
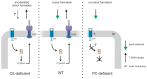
Many cellular processes critically depend on the membrane composition. In this review, we focus on the biosynthesis and physiological roles of membrane lipids in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The major components of A. tumefaciens membranes are the phospholipids (PLs), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylcholine (PC) and cardiolipin, and ornithine lipids (OLs). Under phosphate-limited conditions, the membrane composition shifts to phosphate-free lipids like glycolipids, OLs and a betaine lipid. Remarkably, PC and OLs have opposing effects on virulence of A. tumefaciens. OL-lacking A. tumefaciens mutants form tumors on the host plant earlier than the wild type suggesting a reduced host defense response in the absence of OLs. In contrast, A. tumefaciens is compromised in tumor formation in the absence of PC. In general, PC is a rare component of bacterial membranes but amount to ~22% of all PLs in A. tumefaciens. PC biosynthesis occurs via two pathways. The phospholipid N-methyltransferase PmtA methylates PE via the intermediates monomethyl-PE and dimethyl-PE to PC. In the second pathway, the membrane-integral enzyme PC synthase (Pcs) condenses choline with CDP-diacylglycerol to PC. Apart from the virulence defect, PC-deficient A. tumefaciens pmtA and pcs double mutants show reduced motility, enhanced biofilm formation and increased sensitivity towards detergent and thermal stress. In summary, there is cumulative evidence that the membrane lipid composition of A. tumefaciens is critical for agrobacterial physiology and tumor formation.
Keywords: Agrobacterium tumefaciens; betaine lipids; glycolipids; membrane lipids; ornithine lipids; phosphatidylcholine; phospholipid biosynthesis; phosphorus-free lipids.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression and physiological relevance of Agrobacterium tumefaciens phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis genes.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jan;191(1):365-74. doi: 10.1128/JB.01183-08. Epub 2008 Oct 31. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 18978052 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro characterization of the enzyme properties of the phospholipid N-methyltransferase PmtA from Agrobacterium tumefaciens.J Bacteriol. 2009 Apr;191(7):2033-41. doi: 10.1128/JB.01591-08. Epub 2009 Jan 30. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19181804 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens requires phosphatidylcholine in the bacterial membrane.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Nov;62(3):906-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05425.x. Epub 2006 Sep 29. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17010159
-
Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and function in bacteria.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar;1831(3):503-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.08.009. Epub 2012 Aug 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22922101 Review.
-
Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and its significance in bacteria interacting with eukaryotic cells.Eur J Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;89(12):888-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.06.013. Epub 2010 Jul 24. Eur J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20656373 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterizing the Structure and Interactions of Model Lipid Membranes Using Electrophysiology.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Apr 27;11(5):319. doi: 10.3390/membranes11050319. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33925756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryo-EM structure of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens T4SS-associated T-pilus reveals stoichiometric protein-phospholipid assembly.Structure. 2023 Apr 6;31(4):385-394.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2023.02.005. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Structure. 2023. PMID: 36870333 Free PMC article.
-
Three separate pathways in Rhizobium leguminosarum maintain phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis, which is required for symbiotic nitrogen fixation with clover.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Sep 18;90(9):e0059024. doi: 10.1128/aem.00590-24. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39120150 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: "Agrobacterium biology and its application to transgenic plant production".Front Plant Sci. 2015 Apr 22;6:265. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00265. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25954291 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis in Mitis Group Streptococci via Host Metabolite Scavenging.J Bacteriol. 2019 Oct 21;201(22):e00495-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00495-19. Print 2019 Nov 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31501281 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

