Eribulin mesylate in pretreated breast cancer patients: a multicenter retrospective observational study
- PMID: 24723974
- PMCID: PMC3982178
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.8748
Eribulin mesylate in pretreated breast cancer patients: a multicenter retrospective observational study
Abstract
Background: Eribulin was recently approved in patients progressing after being treated with anthracyclines and taxanes and after two or more chemotherapy lines for advanced disease.
Objectives: This multicenter observational retrospective study was performed in order to evaluate activity and tolerability of eribulin in real-world patient population.
Methods: 133 advanced breast cancer patients pretreated with ≥ 2 chemotherapy lines for metastatic disease were retrospectively enrolled in the observational trial in 11 italian cancer centres.
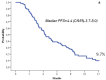
Results: A median of 5 cycles of eribulin (range, 1-15) were administered. Twenty-eight partial responses were observed, for an overall response rate of 21.1% (95%CI,14.1-28.0). A stable disease was recorded in 57 patients (42.8%), and a clinical benefit (response or stable disease lasting ≥ six months) was observed in 51 patients (38.3%, 95%CI, 30.1-46.6). The subgroup analysis showed that a significant improvement in term of partial response and clinical benefit was achieved when eribulin was administered in HER-2 negative tumors (p=0.01 and p=0.004, respectively) and when it is given as third-line (p=0.09 and p=0.02, respectively). Toxicity was manageable; fatigue is the most common side effect observed, usually of low-grade, and clearly cumulative-dose related.
Conclusions: In this retrospective, observational analysis eribulin confirmed its efficacy and manageable tolerability even in real-world population and in heavily pretreated patients.
Keywords: advanced breast cancer; chemotherapy.; eribulin mesylate; heavily pretreated patients; real-world population.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- El Saghir NS, Tfayli A, Hatoum HA, Nachef Z, Dinh P, Awada A. Treatment of metastatic breast cancer: state-of-the-art, subtypes and perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011;80:433–49. - PubMed
-
- Jordan MA, Kamath K, Manna T. et al. The primary antimitotic mechanism of action of the synthetic halichondrin E7389 is suppression of microtubule growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:1086–95. - PubMed
-
- Towle MJ, Salvato KA, Wels BF. et al. Eribulin induces irreversible mitotic blockade: implications of cell-based pharmacodynamics for in vivo efficacy under intermittent dosing conditions. Cancer Res. 2011;71:496–505. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous