Cabozantinib-induced thyroid dysfunction: a review of two ongoing trials for metastatic bladder cancer and sarcoma
- PMID: 24724719
- PMCID: PMC4106376
- DOI: 10.1089/thy.2013.0621
Cabozantinib-induced thyroid dysfunction: a review of two ongoing trials for metastatic bladder cancer and sarcoma
Abstract
Background: Thyroid dysfunction is a common adverse event associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI), but its underlying pathophysiology is unclear. Cabozantinib is a novel TKI currently Food and Drug Administration approved for advanced medullary thyroid cancer and tested in clinical trials on solid tumors including prostate, liver, bladder, breast, and ovarian cancer.
Methods: We analyzed the thyroid function of patients enrolled in two phase 2 clinical trials using cabozantinib at the National Institutes of Health Clinical Center. Two cases of thyroiditis associated with cabozantinib therapy are presented in detail, and a systematic review of the literature on TKI-associated thyroid dysfunction is also discussed.
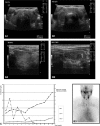
Results: Between September 2012 and September 2013, 33 patients were treated with cabozantinib, and follow-up thyroid function tests were available for 31 (20 males, 11 females; age 59±1 years). Thyroid dysfunction was recorded in the majority of patients (93.1%), with a predominance of subclinical hypothyroidism. Two cases showed a biphasic pattern of thyroid dysfunction characterized by a transient thyrotoxicosis followed by hypothyroidism. Color Doppler demonstrated an increase in vascularization during the thyrotoxic phase, but no uptake was visualized on nuclear medicine imaging. A systematic review of the literature resulted in the identification of 40 original manuscripts, of which 13 were case series and 6 were case reports describing TKI-associated thyroid dysfunction.
Conclusion: TKI therapy often results in clinically significant thyroid dysfunction. Cabozantinib treatment commonly results in thyroid dysfunction varying from subclinical hypothyroidism to symptomatic thyrotoxicosis. Early detection and characterization of cabozantinib-associated thyroid dysfunction and close follow-up are essential to provide adequate management of this common adverse event.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cabozantinib as an emerging treatment for sarcoma.Curr Opin Oncol. 2020 Jul;32(4):321-331. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000644. Curr Opin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32541320 Review.
-
Activity of XL184 (Cabozantinib), an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with medullary thyroid cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2011 Jul 1;29(19):2660-6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.32.4145. Epub 2011 May 23. J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21606412 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cabozantinib for the treatment of progressive metastatic medullary thyroid cancer.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2016;9(1):69-79. doi: 10.1586/17512433.2016.1102052. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26536165 Review.
-
Cabozantinib in progressive medullary thyroid cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2013 Oct 10;31(29):3639-46. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.48.4659. Epub 2013 Sep 3. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24002501 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cabozantinib in Thyroid Cancer.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2015;10(3):259-69. doi: 10.2174/1574892810666150708110816. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2015. PMID: 26152149 Review.
Cited by
-
Cabozantinib-Induced Severe Cardiac Dysfunction: A Case Report and a Systematic Review of the Literature.Cureus. 2022 Apr 1;14(4):e23740. doi: 10.7759/cureus.23740. eCollection 2022 Apr. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35509750 Free PMC article.
-
KRAS and HRAS mutations confer resistance to MET targeting in preclinical models of MET-expressing tumor cells.Mol Oncol. 2015 Aug;9(7):1434-46. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Mol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25933688 Free PMC article.
-
Cabozantinib for neurofibromatosis type 1-related plexiform neurofibromas: a phase 2 trial.Nat Med. 2021 Jan;27(1):165-173. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-01193-6. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Nat Med. 2021. PMID: 33442015 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cabozantinib in patients with platinum-refractory metastatic urothelial carcinoma: an open-label, single-centre, phase 2 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2020 Aug;21(8):1099-1109. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30202-3. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Lancet Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32645282 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The treatment landscape in thyroid cancer: a focus on cabozantinib.Cancer Manag Res. 2015 Aug 19;7:265-78. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S68373. eCollection 2015. Cancer Manag Res. 2015. PMID: 26316818 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Illouz F, Laboureau-Soares S, Dubois S, Rohmer V, Rodien P.2009Tyrosine kinase inhibitors and modifications of thyroid function tests: a review. Eur J Endocrinol 160:331–336 - PubMed
-
- Torino F, Barnabei A, Paragliola RM, Baldelli R, Appetecchia M, Corsello SM.2013Thyroid as unintended side effect of anticancer drugs. Thyroid 23:1345–1366 - PubMed
-
- Ohba K, Takayama T, Matsunaga H, Matsushita A, Sasaki S, Oki Y, Ozono S, Nakamura H.2012Inappropriate elevation of serum thyrotropin levels in patients treated with axitinib. Thyroid 23:443–448 - PubMed
-
- Desai J, Yassa L, Marqusee E, George S, Frates MC, Chen MH, Morgan JA, Dychter SS, Larsen PR, Demetri GD, Alexander EK.2006Hypothyroidism after sunitinib treatment for patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Ann Intern Med 145:660–664 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

