Lack of group X secreted phospholipase A₂ increases survival following pandemic H1N1 influenza infection
- PMID: 24725934
- PMCID: PMC4106042
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.01.030
Lack of group X secreted phospholipase A₂ increases survival following pandemic H1N1 influenza infection
Abstract
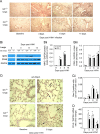
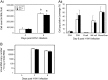
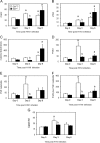
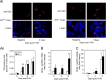
The role of Group X secreted phospholipase A2 (GX-sPLA2) during influenza infection has not been previously investigated. We examined the role of GX-sPLA2 during H1N1 pandemic influenza infection in a GX-sPLA2 gene targeted mouse (GX(-/-)) model and found that survival after infection was significantly greater in GX(-/-) mice than in GX(+/+) mice. Downstream products of GX-sPLA2 activity, PGD2, PGE2, LTB4, cysteinyl leukotrienes and Lipoxin A4 were significantly lower in GX(-/-) mice BAL fluid. Lung microarray analysis identified an earlier and more robust induction of T and B cell associated genes in GX(-/-) mice. Based on the central role of sPLA2 enzymes as key initiators of inflammatory processes, we propose that activation of GX-sPLA2 during H1N1pdm infection is an early step of pulmonary inflammation and its inhibition increases adaptive immunity and improves survival. Our findings suggest that GX-sPLA2 may be a potential therapeutic target during influenza.
Keywords: H1N1 pandemic influenza; Host response; Inflammation; Influenza; Leukotrienes; Lipoxin A(4); Pathogenesis; Phospholipids; Prostaglandins; Secreted phospholipase A(2).
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Baillie J.K., Digard P. Influenza – time to target the host? N. Engl. J. Med. 2013;369:191–193. - PubMed
-
- Bermejo-Martin J.F., Ortiz de L.R., Pumarola T., Rello J., Almansa R., Ramirez P., Martin-Loeches I., Varillas D., Gallegos M.C., Seron C., Micheloud D., Gomez J.M., Tenorio-Abreu A., Ramos M.J., Molina M.L., Huidobro S., Sanchez E., Gordon M., Fernandez V., Del C.A., Marcos M.A., Villanueva B., Lopez C.J., Rodriguez-Dominguez M., Galan J.C., Canton R., Lietor A., Rojo S., Eiros J.M., Hinojosa C., Gonzalez I., Torner N., Banner D., Leon A., Cuesta P., Rowe T., Kelvin D.J. Th1 and Th17 hypercytokinemia as early host response signature in severe pandemic influenza. Crit. Care. 2009;13:R201. (doi:cc8208 [pii];10.1186/cc8208 [doi]) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bermejo-Martin J.F., Martin-Loeches I., Rello J., Anton A., Almansa R., Xu L., Lopez-Campos G., Pumarola T., Ran L., Ramirez P., Banner D., Ng D.C., Socias L., Loza A., Andaluz D., Maravi E., Gomez-Sanchez M.J., Gordon M., Gallegos M.C., Fernandez V., Aldunate S., Leon C., Merino P., Blanco J., Martin-Sanchez F., Rico L., Varillas D., Iglesias V., Marcos M.A., Gandia F., Bobillo F., Nogueira B., Rojo S., Resino S., Castro C., Ortiz de L.R., Kelvin D. Host adaptive immunity deficiency in severe pandemic influenza. Crit. Care. 2010;14:R167. (doi:cc9259 [pii];10.1186/cc9259 [doi]) - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

