Assembling evidence for identifying reservoirs of infection
- PMID: 24726345
- PMCID: PMC4007595
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tree.2014.03.002
Assembling evidence for identifying reservoirs of infection
Abstract
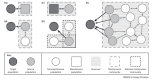
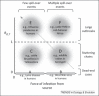
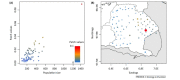
Many pathogens persist in multihost systems, making the identification of infection reservoirs crucial for devising effective interventions. Here, we present a conceptual framework for classifying patterns of incidence and prevalence, and review recent scientific advances that allow us to study and manage reservoirs simultaneously. We argue that interventions can have a crucial role in enriching our mechanistic understanding of how reservoirs function and should be embedded as quasi-experimental studies in adaptive management frameworks. Single approaches to the study of reservoirs are unlikely to generate conclusive insights whereas the formal integration of data and methodologies, involving interventions, pathogen genetics, and contemporary surveillance techniques, promises to open up new opportunities to advance understanding of complex multihost systems.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Woolhouse M.E. Population biology of multihost pathogens. Science. 2001;292:1109–1112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AI047498/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- G0901135/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J010367/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H009035/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H009302/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

