Linsitinib (OSI-906) antagonizes ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2 and subfamily C member 10-mediated drug resistance
- PMID: 24726739
- PMCID: PMC7670583
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.03.026
Linsitinib (OSI-906) antagonizes ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2 and subfamily C member 10-mediated drug resistance
Abstract
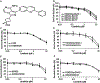
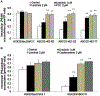
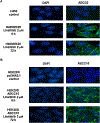
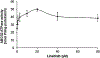
In this study we investigated the effect of linsitinib on the reversal of multidrug resistance (MDR) mediated by the overexpression of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) subfamily members ABCB1, ABCG2, ABCC1 and ABCC10. Our results indicate for the first time that linsitinib significantly potentiate the effect of anti-neoplastic drugs mitoxantrone (MX) and SN-38 in ABCG2-overexpressing cells; paclitaxel, docetaxel and vinblastine in ABCC10-overexpressing cells. Linsitinib moderately enhanced the cytotoxicity of vincristine in cell lines overexpressing ABCB1, whereas it did not alter the cytotoxicity of substrates of ABCC1. Furthermore, linsitinib significantly increased the intracellular accumulation and decreased the efflux of [(3)H]-MX in ABCG2-overexpressing cells and [(3)H]-paclitaxel in ABCC10-overexpressing cells. However, linsitinib, at a concentration that reversed MDR, did not significantly alter the expression levels of either the ABCG2 or ABCC10 transporter proteins. Furthermore, linsitinib did not significantly alter the intracellular localization of ABCG2 or ABCC10. Moreover, linsitinib stimulated the ATPase activity of ABCG2 in a concentration-dependent manner. Overall, our study suggests that linsitinib attenuates ABCG2- and ABCC10-mediated MDR by directly inhibiting their function as opposed to altering ABCG2 or ABCC10 protein expression.
Keywords: ABCC10; ABCG2; Linsitinib; Multi-drug resistance; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
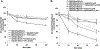
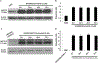
References
-
- Ambudkar SV. Drug-stimulatable ATPase activity in crude membranes of human MDR1-transfected mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol 1998;292:504–14. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 1976;72:248–54. - PubMed
-
- Chen ZS, Robey RW, Belinsky MG, Shchaveleva I, Ren XQ, Sugimoto Y, et al. Transport of methotrexate, methotrexate polyglutamates, and 17beta-estradiol 17-(beta-D-glucuronide) by ABCG2: effects of acquired mutations at R482 on methotrexate transport. Cancer Res 2003;63:4048–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

