The chemical logic of plant natural product biosynthesis
- PMID: 24727074
- PMCID: PMC6863165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbi.2014.03.007
The chemical logic of plant natural product biosynthesis
Abstract
Understanding the logic of plant natural product biosynthesis is important for three reasons: it guides the search for new natural products and pathways, illuminates the function of existing pathways in the context of host biology, and builds an enabling 'parts list' for plant and microbial metabolic engineering. In this review, we highlight the chemical themes that underlie a broad range of plant pathways, dividing pathways into two parts: scaffold-generating steps that draw on a limited set of chemistries, and tailoring reactions that produce a wide range of end products from a small number of common scaffolds.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
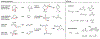
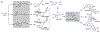

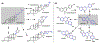
References
-
- Dewick PM: Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach, 3rd Edition. John Wiley and Sons; 2009.
-
- Weng J-K, Philippe RN, Noel JP: The rise of chemodiversity in plants. Science 2012, 336:1667. –1670. - PubMed
-
In this review, authors provide a complementary perspective to the chemical logic of plant metabolism that is highlighted above. They discuss how permissiveness (e.g. ability to accept a broader range of substrates, tolerance to mutations, catalyzing alternative reactions) may partially explain the chemodiversity of plant natural products.
-
- Croteau R, Kutchan TM, Lewis NG: Natural products: Secondary Metabolites In Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Plants. Edited by Buchanan B, Gruissem W, Jones R. American Society of Plant Physiologists; 2000:1250–1318.
-
- Flores-Sanchez IJ, Verpoorte R: Plant Polyketide Synthases: A fascinating group of enzymes. Plant Physiol and Biochem 2009, 47:167–174. - PubMed
-
- Degenhardt J, Kollner TG, Gershenzon J: Monoterpene and sesquiterpene synthases and the origin of terpene skeletal diversity in plants. Phytochem 2009, 70:1621. –1637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

