Erlotinib, erlotinib-sulindac versus placebo: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled window trial in operable head and neck cancer
- PMID: 24727329
- PMCID: PMC4104657
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3360
Erlotinib, erlotinib-sulindac versus placebo: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled window trial in operable head and neck cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The EGF receptor (EGFR) and COX2 pathways are upregulated in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Preclinical models indicate synergistic antitumor activity from dual blockade. We conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled window trial of erlotinib, an EGFR inhibitor; erlotinib plus sulindac, a nonselective COX inhibitor; versus placebo.
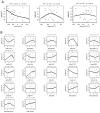
Experimental design: Patients with untreated, operable stage II-IVb HNSCC were randomized 5:5:3 to erlotinib, erlotinib-sulindac, or placebo. Tumor specimens were collected before and after seven to 14 days of treatment. The primary endpoint was change in Ki67 proliferation index. We hypothesized an ordering effect in Ki67 reduction: erlotinib-sulindac > erlotinib > placebo. We evaluated tissue microarrays by immunohistochemistry for pharmacodynamic modulation of EGFR and COX2 signaling intermediates.
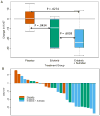
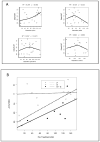
Results: From 2005-2009, 47 patients were randomized for the target 39 evaluable patients. Thirty-four tumor pairs were of sufficient quality to assess biomarker modulation. Ki67 was significantly decreased by erlotinib or erlotinib-sulindac (omnibus comparison, two-sided Kruskal-Wallis, P = 0.04). Wilcoxon pairwise contrasts confirmed greater Ki67 effect in both erlotinib groups (erlotinib-sulindac vs. placebo, P = 0.043; erlotinib vs. placebo, P = 0.027). There was a significant trend in ordering of Ki67 reduction: erlotinib-sulindac > erlotinib > placebo (two-sided exact Jonckheere-Terpstra, P = 0.0185). Low baseline pSrc correlated with greater Ki67 reduction (R(2) = 0.312, P = 0.024).
Conclusions: Brief treatment with erlotinib significantly decreased proliferation in HNSCC, with additive effect from sulindac. Efficacy studies of dual EGFR-COX inhibition are justified. pSrc is a potential resistance biomarker for anti-EGFR therapy, and warrants investigation as a molecular target.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00779389 NCT01488318.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest for the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- Rubin Grandis J, Melhem MF, Gooding WE, Day R, Holst VA, Wagener MM, et al. Levels of TGF-alpha and EGFR protein in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and patient survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90:824–32. - PubMed
-
- Chung CH, Ely K, McGavran L, Varella-Garcia M, Parker J, Parker N, et al. Increased epidermal growth factor receptor gene copy number is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4170–6. - PubMed
-
- Ang KK, Berkey BA, Tu X, Zhang HZ, Katz R, Hammond EH, et al. Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor expression on survival and pattern of relapse in patients with advanced head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:7350–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

