The effect of chitin size, shape, source and purification method on immune recognition
- PMID: 24727416
- PMCID: PMC6271096
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules19044433
The effect of chitin size, shape, source and purification method on immune recognition
Abstract
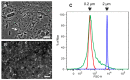
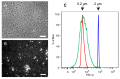
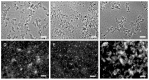
The animal immune response to chitin is not well understood and needs to be investigated further. However, this is a challenging topic to study because of the technical difficulties in purifying chitin, and because this material usually comes associated with contaminating components that can activate the immune system. In this study, improvements to previously described purification protocols were investigated for chitin obtained from different sources, including commercial shellfish, Candida albicans yeast and hyphal cell walls, as well as cell walls of the filamentous fungi Aspergillus fumigatus and Mucor circinelloides. The immune response to these different chitin preparations was tested using human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. In agreement with previous literature, small chitin particles of an average size of 0.2 µm were not immunogenic. On the other hand, bigger chitin particles induced in some cases a pro-inflammatory response. The results of this work suggest that not only the purity and size of the chitin particles, but also their shape can influence immune recognition.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wagner G.P., Lo J., Laine R., Almeder M. Chitin in the epidermal cuticle of a vertebrate (paralipophrys trigloides, blenniidae, teleostei) Experientia. 1993;49:317–319. doi: 10.1007/BF01923410. - DOI
-
- Jang M.-K., Kong B.-G., Jeong Y.-I., Lee C.H., Nah J.-W. Physicochemical characterization of alpha-chitin, beta-chitin, and gamma-chitin separated from natural resources. J. Polym. Sci. 2004;42:3423–3432. doi: 10.1002/pola.20176. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

