The basic leucine zipper domain transcription factor Atf1 directly controls Cdc13 expression and regulates mitotic entry independently of Wee1 and Cdc25 in Schizosaccharomyces pombe
- PMID: 24728197
- PMCID: PMC4054271
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00059-14
The basic leucine zipper domain transcription factor Atf1 directly controls Cdc13 expression and regulates mitotic entry independently of Wee1 and Cdc25 in Schizosaccharomyces pombe
Abstract
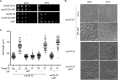
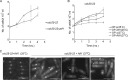
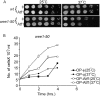
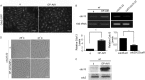
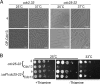
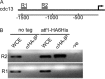
Progression into mitosis is a major point of regulation in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe cell cycle, and its proper control is essential for maintenance of genomic stability. Investigation of the G(2)/M progression event in S. pombe has revealed the existence of a complex regulatory process that is responsible for making the decision to enter mitosis. Newer aspects of this regulation are still being revealed. In this paper, we report the discovery of a novel mode of regulation of G(2)/M progression in S. pombe. We show that the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-regulated transcription factor Atf1 is a regulator of Cdc13 (mitotic cyclin) transcription and is therefore a prominent player in the regulation of mitosis in S. pombe. We have used genetic approaches to study the effect of overexpression or deletion of Atf1 on the cell length and G(2)/M progression of S. pombe cells. Our results clearly show that Atf1 overexpression accelerates mitosis, leading to an accumulation of cells with shorter lengths. The previously known major regulators of entry into mitosis are the Cdc25 phosphatase and the Wee1 kinase, which modulate cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activity. The significantly striking aspect of our discovery is that Atf1-mediated G(2)/M progression is independent of both Cdc25 and Wee1. We have shown that Atf1 binds to the Cdc13 promoter, leading to activation of Cdc13 expression. This leads to enhanced nuclear localization of CDK Cdc2, thereby promoting the G(2)/M transition.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antagonistic regulation of cyclin expression by the bZIP transcription factors Pcr1 and Atf1 during G2/M transition.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2017 Aug 1;364(14). doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnx132. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28645196
-
Transcription factor Atf1-dependent degradation of the mitotic cyclin Cdc13 is regulated by multiple factors in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.FEBS Lett. 2022 Aug;596(16):2021-2030. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14439. Epub 2022 Jul 15. FEBS Lett. 2022. PMID: 35770329
-
spo12 is a multicopy suppressor of mcs3 that is periodically expressed in fission yeast mitosis.Mol Gen Genet. 2000 Oct;264(3):306-16. doi: 10.1007/s004380000324. Mol Gen Genet. 2000. PMID: 11085271
-
Phospho-mimicking Atf1 mutants bypass the transcription activating function of the MAP kinase Sty1 of fission yeast.Curr Genet. 2018 Feb;64(1):97-102. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0730-7. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28799013 Review.
-
Regulation of Cdc2 activity by phosphorylation at T14/Y15.Prog Cell Cycle Res. 1996;2:99-105. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-5873-6_10. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 1996. PMID: 9552387 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Profiling of bZIP Transcription Factors and FocbZIP11's Impact on Fusarium TR4 Pathogenicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 9;26(4):1452. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041452. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003918 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide transcription profiling reveals a major role for the transcription factor Atf1 in regulation of cell division in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Genom Data. 2015 Sep 18;6:184-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gdata.2015.09.014. eCollection 2015 Dec. Genom Data. 2015. PMID: 26697368 Free PMC article.
-
Adding phosphorylation events to the core oscillator driving the cell cycle of fission yeast.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 4;13(12):e0208515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208515. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30513113 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

