Peretinoin after curative therapy of hepatitis C-related hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study
- PMID: 24728665
- PMCID: PMC4318984
- DOI: 10.1007/s00535-014-0956-9
Peretinoin after curative therapy of hepatitis C-related hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study
Abstract
Background: Effective prophylactic therapies have not been established for hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. Peretinoin represents one novel option for patients with hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCV-HCC), and it was tested in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
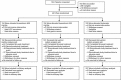
Methods: Patients with curative therapy were assigned to one of the following regimens: peretinoin 600, 300 mg/day, or placebo for up to 96 weeks. The primary outcome was recurrence-free survival (RFS).
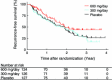
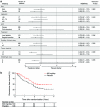
Results: Of the 401 patients initially enrolled, 377 patients were analyzed for efficacy. The RFS rates in the 600-mg group, the 300-mg group, and the placebo group were 71.9, 63.6, and 66.0 % at 1 year, and 43.7, 24.9, and 29.3 % at 3 years, respectively. The primary comparison of peretinoin (300 and 600-mg) with placebo was not significant (P = 0.434). The dose-response relationship based on the hypothesis that "efficacy begins to increase at 600 mg/day" was significant (P = 0.023, multiplicity-adjusted P = 0.048). The hazard ratios for RFS in the 600-mg group vs. the placebo group were 0.73 [95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.51-1.03] for the entire study period and 0.27 (95 % CI 0.07-0.96) after 2 years of the randomization. Common adverse events included ascites, increased blood pressure, headache, presence of urine albumin, and increased transaminases.
Conclusions: Although the superiority of peretinoin to placebo could not be validated, 600 mg/day was shown to be the optimal dose, and treatment may possibly reduce the recurrence of HCV-HCC, particularly after 2 years. The efficacy and safety of peretinoin 600 mg/day should continue to be evaluated in further studies.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical