methylC Track: visual integration of single-base resolution DNA methylation data on the WashU EpiGenome Browser
- PMID: 24728854
- PMCID: PMC4103599
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu191
methylC Track: visual integration of single-base resolution DNA methylation data on the WashU EpiGenome Browser
Abstract
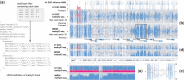
Summary: We present methylC track, an efficient mechanism for visualizing single-base resolution DNA methylation data on a genome browser. The methylC track dynamically integrates the level of methylation, the position and context of the methylated cytosine (i.e. CG, CHG and CHH), strand and confidence level (e.g. read coverage depth in the case of whole-genome bisulfite sequencing data). Investigators can access and integrate these information visually at specific locus or at the genome-wide level on the WashU EpiGenome Browser in the context of other rich epigenomic datasets.
Availability and implementation: The methylC track is part of the WashU EpiGenome Browser, which is open source and freely available at http://epigenomegateway.wustl.edu/browser/. The most up-to-date instructions and tools for preparing methylC track are available at http://epigenomegateway.wustl.edu/+/cmtk.
Contact: twang@genetics.wustl.edu
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Esteller M. Cancer epigenomics: DNA methylomes and histone-modifications maps. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007;8:286–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

