Real-time, in vivo determination of dynamic changes in lung and heart tissue oxygenation using EPR oximetry
- PMID: 24729218
- PMCID: PMC4330333
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0620-8_11
Real-time, in vivo determination of dynamic changes in lung and heart tissue oxygenation using EPR oximetry
Abstract
The use of electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) oximetry for oxygen measurements in deep tissues (>1 cm) is challenging due to the limited penetration depth of the microwave energy. To overcome this limitation, implantable resonators, having a small (0.5 mm diameter) sensory loop containing the oxygen-sensing paramagnetic material connected by a pair of twisted copper wire to a coupling loop (8-10 mm diameter), have been developed, which enable repeated measurements of deep-tissue oxygen levels (pO2, partial pressure of oxygen) in the brain and tumors of rodents. In this study, we have demonstrated the feasibility of measuring dynamic changes in pO2 in the heart and lung of rats using deep-tissue implantable oxygen sensors. The sensory loop of the resonator contained lithium octa-n-butoxynaphthalocyanine (LiNc-BuO) crystals embedded in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) polymer and was implanted in the myocardial tissue or lung pleura. The external coupling loop was secured subcutaneously above chest. The rats were exposed to different breathing gas mixtures while undergoing EPR measurements. The results demonstrated that implantable oxygen sensors provide reliable measurements of pO2 in deep tissues such as heart and lung under adverse conditions of cardiac and respiratory motions.
Figures



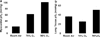
References
-
- Hou H, Dong R, Li H, Williams B, Lariviere JP, Hekmatyar SK, Kauppinen RA, Khan N, Swartz H. Dynamic changes in oxygenation of intracranial tumor and contralateral brain during tumor growth and carbogen breathing: a multisite EPR oximetry with implantable resonators. J Magn Reson. 2012;214:22–28. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pandian RP, Parinandi NL, Ilangovan G, Zweier IL, Kuppusamy P. Novel particulate spin probe for targeted determination of oxygen in cells and tissues. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003;35:1138–1148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

