Analysis of global changes in gene expression induced by human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPase(old-35))
- PMID: 24729470
- PMCID: PMC4149605
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.24645
Analysis of global changes in gene expression induced by human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPase(old-35))
Abstract
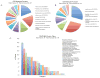
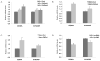
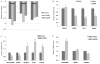
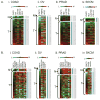
As a strategy to identify gene expression changes affected by human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPase(old-35)), we performed gene expression analysis of HeLa cells in which hPNPase(old-35) was overexpressed. The observed changes were then compared to those of HO-1 melanoma cells in which hPNPase(old-35) was stably knocked down. Through this analysis, 90 transcripts, which positively or negatively correlated with hPNPase(old-35) expression, were identified. The majority of these genes were associated with cell communication, cell cycle, and chromosomal organization gene ontology categories. For a number of these genes, the positive or negative correlations with hPNPase(old-35) expression were consistent with transcriptional data extracted from the TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) expression datasets for colon adenocarcinoma (COAD), skin cutaneous melanoma (SKCM), ovarian serous cyst adenocarcinoma (OV), and prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD). Further analysis comparing the gene expression changes between Ad.hPNPase(old-35) infected HO-1 melanoma cells and HeLa cells overexpressing hPNPase(old-35) under the control of a doxycycline-inducible promoter, revealed global changes in genes involved in cell cycle and mitosis. Overall, this study provides further evidence that hPNPase(old-35) is associated with global changes in cell cycle-associated genes and identifies potential gene targets for future investigation.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of genes potentially regulated by human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPase old-35) using melanoma as a model.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 15;8(10):e76284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076284. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24143183 Free PMC article.
-
Expression regulation and genomic organization of human polynucleotide phosphorylase, hPNPase(old-35), a Type I interferon inducible early response gene.Gene. 2003 Oct 16;316:143-56. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(03)00752-2. Gene. 2003. PMID: 14563561
-
Defining the mechanism by which IFN-beta dowregulates c-myc expression in human melanoma cells: pivotal role for human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPaseold-35).Cell Death Differ. 2006 Sep;13(9):1541-53. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401829. Epub 2006 Jan 13. Cell Death Differ. 2006. PMID: 16410805
-
Human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPase old-35): an RNA degradation enzyme with pleiotrophic biological effects.Cell Cycle. 2006 May;5(10):1080-4. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.10.2741. Epub 2006 May 15. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16687933 Review.
-
Polynucleotide phosphorylase: an evolutionary conserved gene with an expanding repertoire of functions.Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Oct;112(1):243-63. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.04.003. Epub 2006 Jun 2. Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16733069 Review.
Cited by
-
[Role of PNPT1 in cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 Apr 20;42(4):584-590. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.04.15. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35527495 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Prevention of dsRNA-induced interferon signaling by AGO1x is linked to breast cancer cell proliferation.EMBO J. 2020 Sep 15;39(18):e103922. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019103922. Epub 2020 Aug 19. EMBO J. 2020. PMID: 32812257 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Therapies for Cancer: Strategies, Challenges and Successes.J Cell Physiol. 2015 Feb;230(2):259-71. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24791. J Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25196387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenomic portals for the visualization and analysis of genome-wide cancer data.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 5;7(1):176-92. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6128. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26484415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PNPase knockout results in mtDNA loss and an altered metabolic gene expression program.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 19;13(7):e0200925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200925. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30024931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrade J, Pobre V, Silva I, Domingues S, Arraiano C. The role of 3′-5′ exoribonucleases in RNA degradation. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2009;85:187–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

