A silencer-proximal intronic region is required for sustained CD4 expression in postselection thymocytes
- PMID: 24729613
- PMCID: PMC4052224
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302374
A silencer-proximal intronic region is required for sustained CD4 expression in postselection thymocytes
Abstract
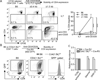
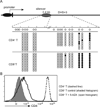
It has been proposed that differential kinetics of CD4/CD8 coreceptors regulate fate choice of selected thymocytes. Sustained signals by interaction between MHC class II and TCR/CD4 is required for commitment to the CD4 helper lineage. Although prematurely terminated MHC-TCR/CD4 interaction in transgenic mouse models results in lineage redirection, it is unclear whether CD4 expression is actively maintained by endogenous cis-elements to facilitate prolonged signaling under physiological conditions. In this article, we show that sustained CD4 expression in postselection thymocytes requires an intronic sequence containing an uncharacterized DNase I hypersensitivity (DHS) site located 3' to the silencer. Despite normal CD4 expression before selection, thymocytes lacking a 1.5-kb sequence in intron 1 including the 0.4-kb silencer and the DHS, but not the 0.4-kb silencer alone, failed to maintain CD4 expression upon positive selection and are redirected to the CD8 lineage after MHC class II-restricted selection. Furthermore, CpG dinucleotides adjacent to the DHS are hypermethylated in CD8(+) T cells. These results indicate that the 1.5-kb cis-element is required in postselection thymocytes for helper lineage commitment, presumably mediating the maintenance of CD4 expression, and suggest that inactivation of the cis-element by DNA methylation may contribute to epigenetic Cd4 silencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kappes DJ, He X, He X. CD4-CD8 lineage commitment: an inside view. Nature immunology. 2005;6:761–766. - PubMed
-
- Brugnera E, Bhandoola A, Cibotti R, Yu Q, Guinter TI, Yamashita Y, Sharrow SO, Singer A. Coreceptor reversal in the thymus: signaled CD4+8+ thymocytes initially terminate CD8 transcription even when differentiating into CD8+ T cells. Immunity. 2000;13:59–71. - PubMed
-
- Kioussis D, Ellmeier W. Chromatin and CD4, CD8A and CD8B gene expression during thymic differentiation. Nature reviews. Immunology. 2002;2:909–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

