Improving Reproducibility of Lab-on-a-Chip Sensor with Bismuth Working Electrode for Determining Zn in Serum by Anodic Stripping Voltammetry
- PMID: 24729629
- PMCID: PMC3980724
- DOI: 10.1149/2.022402jes
Improving Reproducibility of Lab-on-a-Chip Sensor with Bismuth Working Electrode for Determining Zn in Serum by Anodic Stripping Voltammetry
Abstract
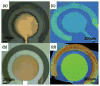
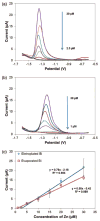
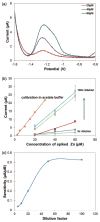
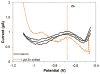
This work reports on the continuing development of a lab-on-a-chip electrochemical sensor for determination of zinc in blood serum using square wave anodic stripping voltammetry. The microscale sensor consists of a three electrode system, including an environmentally friendly bismuth working electrode, an integrated silver/silver chloride reference electrode, and a gold auxiliary electrode. The sensor demonstrates a linear response in 0.1 M acetate buffer at pH 6 for zinc concentrations in the 1-30 μM range. By optimizing bismuth film deposition and better control of the fabrication process, repeatability of the sensor was improved, reducing variability from 42% to <2%. Through optimization of electrolyte and stripping voltammetry parameters, limit of detection was greatly improved to 60 nM. The optimized sensor was also able to measure zinc in the extracted blood serum. Ultimately, with integrated sample preparation, the sensor will permit rapid (min) measurements of zinc from a sub-mL sample (a few drops of blood) for clinical applications.
Figures


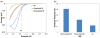
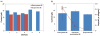
References
-
- Smith JC, Butrimovitz GP, Purdy WC. Clin Chem. 1979;25(8):1487. - PubMed
-
- Rahman S, Waheed S. J Radioanal Nucl Ch. 2009;279(3):915.
-
- Jenner GA, Longerich HP, Jackson SE, Fryer BJ. Chem Geol. 1990;83(1–2):133.
-
- Barany E, Bergdahl IA, Schütz A, Skerfving S, Oskarsson A. J Anal Atom Spectrom. 1997;12(9):1005.
-
- Wang J. Analytical Electrochemistry. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; Hoboken, New Jersey, USA: 2006.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
