Progressive dysphagia and neck pain due to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis of the cervical spine: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 24729695
- PMCID: PMC3976210
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S60146
Progressive dysphagia and neck pain due to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis of the cervical spine: a case report and literature review
Abstract
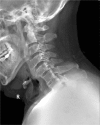
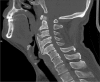
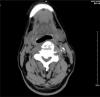
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is considered an underdiagnosed and mostly asymptomatic nonprimary osteoarthritis. The etiology of DISH remains unknown and the validated diagnostic criteria are absent. This condition is still recognized radiologically only. Rarely, large projecting anterior osteophytes result in esophageal impingement and distortion leading to dysphagia. We report the case of progressive dysphagia and neck pain due to DISH of the cervical spine in a 70-year-old man, which was surgically removed with excellent postoperative results and complete resolution of symptoms. Imaging studies, surgical findings, and histopathological examinations were used to support the diagnosis. The patient was successfully treated with total excision of the anterior osteophytes with no evidence of recurrence 12 months after surgery. In this report, we also discuss the clinical features and perioperative considerations in combination with a literature review. Our patient illustrates that clinicians should be aware of this rare clinical manifestation as the presenting feature of DISH in cervical spine. Surgical decompression through osteophytectomy is effective for patients who fail conservative treatment.
Keywords: cervical spine; diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis; dysphagia.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Surgical management of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) causing secondary dysphagia (Narrative review).J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2021 Sep-Dec;29(3):23094990211041783. doi: 10.1177/23094990211041783. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2021. PMID: 34592856 Review.
-
Long-term results after surgical treatment of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) causing dysphagia.J Clin Neurosci. 2019 Sep;67:151-155. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2019.05.057. Epub 2019 Jun 17. J Clin Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31221580
-
Cervical spinal cord injury following osteophyte excision for respiratory distress caused by diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis associated with ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament: a case report and literature review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Dec 19;25(1):1023. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-08134-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39702249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term results of surgical treatment of dysphagia secondary to cervical diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis.Spine J. 2009 Sep;9(9):e13-7. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2009.04.006. Epub 2009 May 28. Spine J. 2009. PMID: 19477693
-
Dysphagia due to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis of the cervical spine.Turk Neurosurg. 2008 Oct;18(4):409-11. Turk Neurosurg. 2008. PMID: 19107690
Cited by
-
Dysphagia in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Mar 6;9(7):1639-1645. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i7.1639. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 33728307 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged Dysphagia due to a Combination of Cerebral Hemorrhage and Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis: A Case Report.NMC Case Rep J. 2016 May 19;3(3):75-79. doi: 10.2176/nmccrj.cr.2016-0024. eCollection 2016 Jul. NMC Case Rep J. 2016. PMID: 28664003 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Respiratory Distress in a Hospitalized Patient Revealing Cervical Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH).Cureus. 2025 Jun 30;17(6):e87042. doi: 10.7759/cureus.87042. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40741575 Free PMC article.
-
Cervical spine fracture in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: A bibliometric analysis.SAGE Open Med. 2024 May 23;12:20503121241249050. doi: 10.1177/20503121241249050. eCollection 2024. SAGE Open Med. 2024. PMID: 38799004 Free PMC article.
-
Symptomatic dyspnoea addressed by excision of ossified anterior longitudinal ligament.BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Jun 20;2018:bcr2017223322. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-223322. BMJ Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29930166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mader R, Verlaan JJ, Buskila D. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: clinical features and pathogenic mechanisms. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013;9(12):741–750. - PubMed
-
- Childs SG. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: Forestier’s disease. Orthop Nurs. 2004;23(6):375–382. - PubMed
-
- Presutti L, Alicandri-Ciufelli M, Piccinini A, et al. Forestier disease: single-center surgical experience and brief literature review. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2010;119(9):602–608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

