Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson's disease: evaluation, management, and emerging role of droxidopa
- PMID: 24729712
- PMCID: PMC3979788
- DOI: 10.2147/VHRM.S53983
Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson's disease: evaluation, management, and emerging role of droxidopa
Abstract
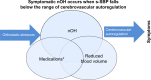
Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension (nOH) is due to failure of the autonomic nervous system to regulate blood pressure in response to postural changes due to an inadequate release of norepinephrine, leading to orthostatic hypotension and supine hypertension. nOH is common in Parkinson's disease (PD). Prevalence varies throughout the course of PD, ranging from 40% to 60%, and resulting in symptomatic nOH in approximately half. Symptomatic nOH, including lightheadedness, can limit daily activities and lead to falls. Symptomatic nOH can also limit therapeutic options for treating PD motor symptoms. Clinical evaluation should routinely include symptom assessment and blood pressure measurement of supine, sitting, and 3-minute standing; 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring can also be helpful. Non-pharmacological management of symptomatic nOH involves education, physical maneuvers, and adequate hydration. Current pharmacological treatment of symptomatic nOH includes salt supplement, fludrocortisone, midodrine, pyridostigmine, and other empiric medications. Despite these options, treatment of symptomatic nOH remains suboptimal, often limited by severe increases in supine blood pressure. Droxidopa, an oral prodrug converted by decarboxylation to norepinephrine, is a promising therapeutic option for symptomatic nOH in PD, improving symptoms of nOH, daily activities, falls, and standing systolic blood pressure in several recent trials. These trials demonstrated short-term efficacy and tolerability, with comparable increases in standing and supine blood pressures. Longer-term studies are ongoing to confirm durability of treatment effect.
Keywords: (pre)syncope; autonomic; falls; lightheadedness; norepinephrine; treatment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diagnosing and treating neurogenic orthostatic hypotension in primary care.Postgrad Med. 2015;127(7):702-15. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2015.1050340. Epub 2015 May 27. Postgrad Med. 2015. PMID: 26012731 Review.
-
Droxidopa for neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial.Neurology. 2014 Jul 22;83(4):328-35. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000615. Epub 2014 Jun 18. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 24944260 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Droxidopa for the short-term treatment of symptomatic neurogenic orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson's disease (nOH306B).Mov Disord. 2015 Apr 15;30(5):646-54. doi: 10.1002/mds.26086. Epub 2014 Dec 9. Mov Disord. 2015. PMID: 25487613 Clinical Trial.
-
Droxidopa in patients with neurogenic orthostatic hypotension associated with Parkinson's disease (NOH306A).J Parkinsons Dis. 2014;4(1):57-65. doi: 10.3233/JPD-130259. J Parkinsons Dis. 2014. PMID: 24326693 Clinical Trial.
-
Standing and Supine Blood Pressure Outcomes Associated With Droxidopa and Midodrine in Patients With Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension: A Bayesian Meta-analysis and Mixed Treatment Comparison of Randomized Trials.Ann Pharmacother. 2018 Dec;52(12):1182-1194. doi: 10.1177/1060028018786954. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Ann Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29972032
Cited by
-
Designer receptors enhance memory in a mouse model of Down syndrome.J Neurosci. 2015 Jan 28;35(4):1343-53. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2658-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25632113 Free PMC article.
-
Role of nurses and nurse practitioners in the recognition, diagnosis, and management of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension: a narrative review.Int J Gen Med. 2019 May 1;12:173-184. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S170655. eCollection 2019. Int J Gen Med. 2019. PMID: 31118743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fuzzy logic-based risk of fall estimation using smartwatch data as a means to form an assistive feedback mechanism in everyday living activities.Healthc Technol Lett. 2016 Nov 30;3(4):263-268. doi: 10.1049/htl.2016.0064. eCollection 2016 Dec. Healthc Technol Lett. 2016. PMID: 28008361 Free PMC article.
-
Toxin Induced Parkinsonism and Hospitalization Related Adverse Outcome Mitigation for Parkinson's Disease: A Comprehensive Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 30;12(3):1074. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031074. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of the symptoms of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension and their impact from a survey of patients and caregivers.BMC Neurol. 2018 Aug 25;18(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12883-018-1129-x. BMC Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30144800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sithinamsuwan P, Orrawanhanothai P, Thithum K, et al. Orthostatic hypotension: a non-motor complication assessment in 82 patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease in Phramongkutklao Hospital. J Med Assoc Thai. 2010;93(Suppl 6):S93–S99. - PubMed
-
- Ha AD, Brown CH, York MK, Jankovic J. The prevalence of symptomatic orthostatic hypotension in patients with Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonism. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2011;17(8):625–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

