Treadmill exercise ameliorates short-term memory disturbance in scopolamine-induced amnesia rats
- PMID: 24729923
- PMCID: PMC3983504
- DOI: 10.5213/inj.2014.18.1.16
Treadmill exercise ameliorates short-term memory disturbance in scopolamine-induced amnesia rats
Abstract
Purpose: Scopolamine is a nonselective muscarinic cholinergic receptor antagonist, which induces impairment of learning ability and memory function. Exercise is known to ameliorate brain disturbance induced by brain injuries. In the present study, we investigated the effect of treadmill exercise on short-term memory in relation to acetylcholinesterase (AChE) expression in the hippocampus, using a scopolamine-induced amnesia model in mice.
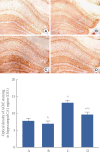
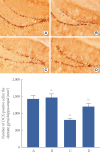
Methods: To induce amnesia, 1 mg/kg scopolamine hydrobromide was administered intraperitoneally once per day for 14 days. A step-down avoidance test for short-term memory was conducted. AChE histochemistry, immunohistochemistry for collagen IV, and doublecortin were performed.
Results: Short-term memory deteriorated in the mice with scopolamine-induced amnesia, concomitant with enhanced AChE expression and suppression of angiogenesis in the hippocampus. Critically, treadmill exercise ameliorated short-term memory impairment, suppressed AChE expression, and enhanced angiogenesis in the mice with scopolamine-induced amnesia.
Conclusions: Overexpression of AChE is implicated in both brain and renal disease. The findings of our study indicate that treadmill exercise may be of therapeutic value in neurodegenerative and renal diseases by suppressing the effects of AChE expression.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase; Amnesia; Exercise test; Short-term memory.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Howes MJ, Perry NS, Houghton PJ. Plants with traditional uses and activities, relevant to the management of Alzheimer's disease and other cognitive disorders. Phytother Res. 2003;17:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Kim MJ, Choi SJ, Lim ST, Kim HK, Kim YJ, Yoon HG, et al. Zeatin supplement improves scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008;72:577–581. - PubMed
-
- Court J, Martin-Ruiz C, Piggott M, Spurden D, Griffiths M, Perry E. Nicotinic receptor abnormalities in Alzheimer's disease. Biol Psychiatry. 2001;49:175–184. - PubMed
-
- Mulugeta E, Karlsson E, Islam A, Kalaria R, Mangat H, Winblad B, et al. Loss of muscarinic M4 receptors in hippocampus of Alzheimer patients. Brain Res. 2003;960:259–262. - PubMed
-
- Araujo JA, Studzinski CM, Milgram NW. Further evidence for the cholinergic hypothesis of aging and dementia from the canine model of aging. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2005;29:411–422. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

