Identifying gastric cancer related genes using the shortest path algorithm and protein-protein interaction network
- PMID: 24729971
- PMCID: PMC3963223
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/371397
Identifying gastric cancer related genes using the shortest path algorithm and protein-protein interaction network
Abstract
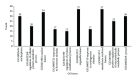
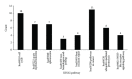
Gastric cancer, as one of the leading causes of cancer related deaths worldwide, causes about 800,000 deaths per year. Up to now, the mechanism underlying this disease is still not totally uncovered. Identification of related genes of this disease is an important step which can help to understand the mechanism underlying this disease, thereby designing effective treatments. In this study, some novel gastric cancer related genes were discovered based on the knowledge of known gastric cancer related ones. These genes were searched by applying the shortest path algorithm in protein-protein interaction network. The analysis results suggest that some of them are indeed involved in the biological process of gastric cancer, which indicates that they are the actual gastric cancer related genes with high probability. It is hopeful that the findings in this study may help promote the study of this disease and the methods can provide new insights to study various diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Estimating the world cancer burden: globocan 2000. International Journal of Cancer. 2001;94(2):153–156. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Shin H-R, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: globocan 2008. International Journal of Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Palli D. Epidemiology of gastric cancer: an evaluation of available evidence. Journal of Gastroenterology. 2000;35(supplement 12):84–89. - PubMed
-
- El-Omar EM, Carrington M, Chow W-H, et al. Interleukin-1 polymorphisms associated with increased risk of gastric cancer. Nature. 2000;404(6776):398–402. - PubMed
-
- Nomura A, Grove JS, Stemmermann GN, Severson RK. Cigarette smoking and stomach cancer. Cancer Research. 1990;50(article 7084) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

