Noncoding RNAs: emerging players in muscular dystrophies
- PMID: 24729974
- PMCID: PMC3960514
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/503634
Noncoding RNAs: emerging players in muscular dystrophies
Abstract
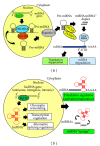
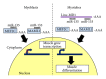
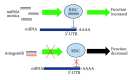
The fascinating world of noncoding RNAs has recently come to light, thanks to the development of powerful sequencing technologies, revealing a variety of RNA molecules playing important regulatory functions in most, if not all, cellular processes. Many noncoding RNAs have been implicated in regulatory networks that are determinant for skeletal muscle differentiation and disease. In this review, we outline the noncoding RNAs involved in physiological mechanisms of myogenesis and those that appear dysregulated in muscle dystrophies, also discussing their potential use as disease biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Figures
References
-
- Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nature Cell Biology. 2009;11(3):228–234. - PubMed
-
- Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nature Reviews Genetics. 2010;11(9):597–610. - PubMed
-
- Pasquinelli AE. MicroRNAs and their targets: recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal relationship. Nature Reviews Genetics. 2012;13(4):271–282. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J, et al. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature. 2003;425(6956):415–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical