Exploration of type II binding mode: A privileged approach for kinase inhibitor focused drug discovery?
- PMID: 24730530
- PMCID: PMC4068218
- DOI: 10.1021/cb500129t
Exploration of type II binding mode: A privileged approach for kinase inhibitor focused drug discovery?
Abstract
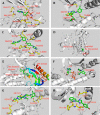
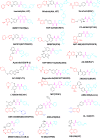
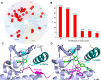
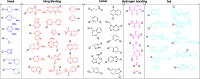
The ATP site of kinases displays remarkable conformational flexibility when accommodating chemically diverse small molecule inhibitors. The so-called activation segment, whose conformation controls catalytic activity and access to the substrate binding pocket, can undergo a large conformational change with the active state assuming a 'DFG-in' and an inactive state assuming a 'DFG-out' conformation. Compounds that preferentially bind to the DFG-out conformation are typically called 'type II' inhibitors in contrast to 'type I' inhibitors that bind to the DFG-in conformation. This review surveys the large number of type II inhibitors that have been developed and provides an analysis of their crystallographically determined binding modes. Using a small library of type II inhibitors, we demonstrate that more than 200 kinases can be targeted, suggesting that type II inhibitors may not be intrinsically more selective than type I inhibitors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploration of structural requirements for the inhibition of VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase: Binding site analysis of type II, 'DFG-out' inhibitors.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Aug;40(12):5712-5727. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1872417. Epub 2021 Jan 18. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 33459187 Review.
-
Conformational analysis of the DFG-out kinase motif and biochemical profiling of structurally validated type II inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2015 Jan 8;58(1):466-79. doi: 10.1021/jm501603h. Epub 2014 Dec 12. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25478866 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting inactive conformations of protein kinases using active structures: conformational selection of type-II inhibitors.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22644. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022644. Epub 2011 Jul 27. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21818358 Free PMC article.
-
Lead Discovery of Type II BRAF V600E Inhibitors Targeting the Structurally Validated DFG-Out Conformation Based upon Selected Fragments.Molecules. 2016 Jul 16;21(7):879. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070879. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27438814 Free PMC article.
-
New insights in protein kinase conformational dynamics.Curr Top Med Chem. 2012;12(17):1889-95. doi: 10.2174/156802612804547407. Curr Top Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 23116468 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of potent Plasmodium falciparum protein kinase 6 (PfPK6) inhibitors with a type II inhibitor pharmacophore.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Mar 5;249:115043. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.115043. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36736152 Free PMC article.
-
Versatile small molecule kinase assay through real-time, ratiometric fluorescence changes based on a pyrene-DPA-Zn2+ complex.RSC Adv. 2021 Mar 10;11(17):10375-10380. doi: 10.1039/d1ra01547h. eCollection 2021 Mar 5. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35423495 Free PMC article.
-
The Development of AXL Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: Recent Progress and Challenges.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 3;12:811247. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.811247. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35311091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DFGmodel: predicting protein kinase structures in inactive states for structure-based discovery of type-II inhibitors.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Jan 16;10(1):269-78. doi: 10.1021/cb500696t. Epub 2014 Dec 9. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25420233 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insight into selectivity and resistance profiles of ROS1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 29;112(39):E5381-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1515281112. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26372962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams J. A. (2001) Kinetic and catalytic mechanisms of protein kinases. Chem. Rev. 101, 2271–2290. - PubMed
-
- Barf T.; Kaptein A. (2012) Irreversible protein kinase inhibitors: balancing the benefits and risks. J. Med. Chem. 55, 6243–6262. - PubMed
-
- Fabbro D.; Cowan-Jacob S. W.; Mobitz H.; Martiny-Baron G. (2012) Targeting cancer with small-molecular-weight kinase inhibitors. Methods Mol. Biol. 795, 1–34. - PubMed
-
- van Linden O. P.; Kooistra A. J.; Leurs R.; de Esch I. J.; de Graaf C. (2014) KLIFS: a knowledge-based structural database to navigate kinase-ligand interaction space. J. Med. Chem. 57, 249–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

