The comparative effectiveness of individual and group brief motivational interventions for mandated college students
- PMID: 24731111
- PMCID: PMC4062841
- DOI: 10.1037/a0034899
The comparative effectiveness of individual and group brief motivational interventions for mandated college students
Abstract
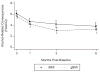
Individual brief motivational intervention (iBMI) is an efficacious strategy to reduce heavy drinking by students who are mandated to receive an alcohol intervention following an alcohol-related event. However, despite the strong empirical support for iBMI, it is unknown if the results from rigorously controlled research on iBMI translate to real-world settings. Furthermore, many colleges lack the resources to provide iBMI to mandated students. Therefore, group-delivered BMI (gBMI) might be a cost-effective alternative that can be delivered to a large number of individuals. The purpose of this study was to conduct a comparative effectiveness evaluation of iBMI and gBMI as delivered by staff at a university health services center. Participants (N = 278) were college students who were mandated to receive an alcohol intervention following an alcohol-related incident. Participants were randomized to receive an individual (iBMI; n = 133) or a Group BMI (gBMI; n = 145). Results indicated that both iBMI and gBMI participants reduced their peak estimated blood alcohol concentration (BAC) and the number of negative alcohol-related consequences at 1-, 3-, and 6-months postintervention. The iBMI and gBMI conditions were not significantly different at follow-up. These findings provide preliminary support for the use of iBMI and gBMIs for college students in real-world settings.
Figures


References
-
- Abrams DB, Orleans CT, Niaura RS, Goldstein MG, Prochaska JO, Velicer W. Integrating individual and public health perspectives for treatment of tobacco dependence under managed health care: A combined stepped-care and matching model. Annals of Behavioral Medicine. 1996;18:290–304. doi: 10.1007/BF02895291. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Babor TF, Higgins-Biddle JC. Brief intervention for hazardous and harmful drinking: A manual for use in primary care. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

