Vascular histone deacetylation by pharmacological HDAC inhibition
- PMID: 24732587
- PMCID: PMC4120081
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.168781.113
Vascular histone deacetylation by pharmacological HDAC inhibition
Abstract
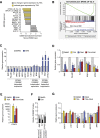
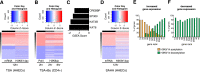
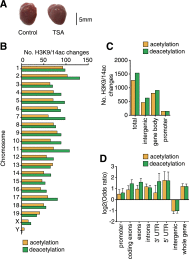
HDAC inhibitors can regulate gene expression by post-translational modification of histone as well as nonhistone proteins. Often studied at single loci, increased histone acetylation is the paradigmatic mechanism of action. However, little is known of the extent of genome-wide changes in cells stimulated by the hydroxamic acids, TSA and SAHA. In this article, we map vascular chromatin modifications including histone H3 acetylation of lysine 9 and 14 (H3K9/14ac) using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) coupled with massive parallel sequencing (ChIP-seq). Since acetylation-mediated gene expression is often associated with modification of other lysine residues, we also examined H3K4me3 and H3K9me3 as well as changes in CpG methylation (CpG-seq). RNA sequencing indicates the differential expression of ∼30% of genes, with almost equal numbers being up- and down-regulated. We observed broad deacetylation and gene expression changes conferred by TSA and SAHA mediated by the loss of EP300/CREBBP binding at multiple gene promoters. This study provides an important framework for HDAC inhibitor function in vascular biology and a comprehensive description of genome-wide deacetylation by pharmacological HDAC inhibition.
© 2014 Rafehi et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures



References
-
- Almeida AM, Murakami Y, Baker A, Maeda Y, Roberts IA, Kinoshita T, Layton DM, Karadimitris A. 2007. Targeted therapy for inherited GPI deficiency. N Engl J Med 356: 1641–1647 - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. 1995. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 57: 289–300
-
- Blanco-Garcia N, Asensio-Juan E, de la Cruz X, Martinez-Balbas MA. 2009. Autoacetylation regulates P/CAF nuclear localization. J Biol Chem 284: 1343–1352 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
