Elimination of inter-domain interactions increases the cleavage fidelity of the restriction endonuclease DraIII
- PMID: 24733184
- PMCID: PMC3996161
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-014-0038-z
Elimination of inter-domain interactions increases the cleavage fidelity of the restriction endonuclease DraIII
Abstract
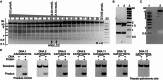
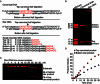
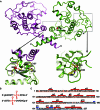
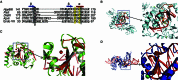
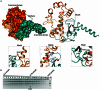
DraIII is a type IIP restriction endonucleases (REases) that recognizes and creates a double strand break within the gapped palindromic sequence CAC↑NNN↓GTG of double-stranded DNA (↑ indicates nicking on the bottom strand; ↓ indicates nicking on the top strand). However, wild type DraIII shows significant star activity. In this study, it was found that the prominent star site is CAT↑GTT↓GTG, consisting of a star 5' half (CAT) and a canonical 3' half (GTG). DraIII nicks the 3' canonical half site at a faster rate than the 5' star half site, in contrast to the similar rate with the canonical full site. The crystal structure of the DraIII protein was solved. It indicated, as supported by mutagenesis, that DraIII possesses a ββα-metal HNH active site. The structure revealed extensive intra-molecular interactions between the N-terminal domain and the C-terminal domain containing the HNH active site. Disruptions of these interactions through site-directed mutagenesis drastically increased cleavage fidelity. The understanding of fidelity mechanisms will enable generation of high fidelity REases.
Figures
References
-
- Adams PD, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Hung LW, Ioerger TR, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Read RJ, Sacchettini JC, Sauter NK, Terwilliger TC. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2002;58:1948–1954. - PubMed
-
- Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4 The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. 1994;50:760–763. - PubMed
-
- Cowtan KD. DM: an automated procedure for phase improvement by density modification. CCP4 Newslett. 1994;31:34–38.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

