Exchange kinetics by inversion transfer: integrated analysis of the phosphorus metabolite kinetic exchanges in resting human skeletal muscle at 7 T
- PMID: 24733433
- PMCID: PMC4197187
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.25256
Exchange kinetics by inversion transfer: integrated analysis of the phosphorus metabolite kinetic exchanges in resting human skeletal muscle at 7 T
Abstract
Purpose: To develop an inversion pulse-based, chemical exchange saturation transfer-like method for detection of (31) P magnetization exchanges among all nuclear magnetic resonance visible metabolites suitable for providing an integrated kinetic analysis of phosphorus exchange reactions in vivo.
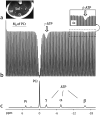
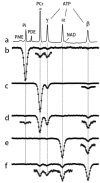
Methods: The exchange kinetics by inversion transfer (EKIT) sequence includes application of a frequency-selective inversion pulse arrayed over the range of relevant (31) P frequencies, followed by a constant delay and a hard readout pulse. A series of EKIT spectra, each given by a plot of Z-magnetization for each metabolite of interest versus frequency of the inversion pulse, can be generated from this single data set.
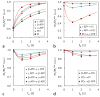
Results: EKIT spectra reflect chemical exchange due to known biochemical reactions, cross-relaxation effects, and relayed magnetization transfers due to both processes. The rate constants derived from EKIT data collected on resting human skeletal muscle were: ATP synthesis via ATP synthase (0.050 ± 0.016 s(-1) ), ATP synthesis via creatine kinase (0.264 ± 0.023 s(-1) ), and cross-relaxation between neighboring spin pairs within ATP (0.164 ± 0.022 s(-1) ).
Conclusion: EKIT provides a simple, alternative method to detect chemical exchange, cross relaxation, and relayed magnetization transfer effects in human skeletal muscle at 7 T.
Keywords: T1 relaxation time; chemical exchange; magnetization transfer; nuclear Overhauser effects; skeletal muscle.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Brindle KM, Radda GK. Measurements of exchange in the reaction catalysed by creatine kinase using 14C and 15N isotope labels and the NMR technique of saturation transfer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;829(2):188–201. - PubMed
-
- Brindle KM, Blackledge MJ, Challiss RA, Radda GK. 31P NMR magnetization-transfer measurements of ATP turnover during steady-state isometric muscle contraction in the rat hind limb in vivo. Biochemistry. 1989;28(11):4887–93. - PubMed
-
- Shoubridge EA, Briggs RW, Radda GK. 31p NMR saturation transfer measurements of the steady state rates of creatine kinase and ATP synthetase in the rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1982;140(2):289–92. - PubMed
-
- Schmid AI, Schrauwen-Hinderling VB, Andreas M, Wolzt M, Moser E, Roden M. Comparison of measuring energy metabolism by different (31) P-magnetic resonance spectroscopy techniques in resting, ischemic, and exercising muscle. Magn Reson Med. 2012;67(4):898–905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

