Pharmacokinetics of prophylactic cefazolin in parturients undergoing cesarean delivery
- PMID: 24733461
- PMCID: PMC4068446
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02613-13
Pharmacokinetics of prophylactic cefazolin in parturients undergoing cesarean delivery
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Elkomy et al., Pharmacokinetics of prophylactic cefazolin in parturients undergoing cesarean delivery.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Jun;59(6):3694. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00585-15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25977453 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
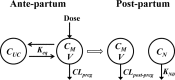
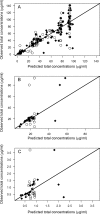
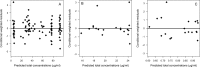
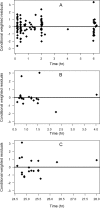
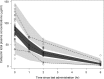
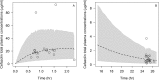
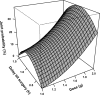
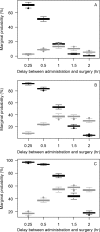
The objectives of this work were (i) to characterize the pharmacokinetics of cefazolin in pregnant women undergoing elective cesarean delivery and in their neonates; (ii) to assess cefazolin transplacental transmission; (iii) to evaluate the dosing and timing of preoperative, prophylactic administration of cefazolin to pregnant women; and (iv) to investigate the impact of maternal dosing on therapeutic duration and exposure in newborns. Twenty women received 1 g of cefazolin preoperatively. Plasma concentrations of total cefazolin were analyzed from maternal blood samples taken before, during, and after delivery; umbilical cord blood samples obtained at delivery; and neonatal blood samples collected 24 h after birth. The distribution volume of cefazolin was 9.44 liters. [corrected] The values for pre- and postdelivery clearance were 7.18 and 4.12 liters/h, respectively. Computer simulations revealed that the probability of maintaining free cefazolin concentrations in plasma above 8 mg/liter during scheduled caesarean surgery was <50% in the cord blood when cefazolin was administered in doses of <2 g or when it was administered <1 h before delivery. Therapeutic concentrations of cefazolin persisted in neonates >5 h after birth. Cefazolin clearance increases during pregnancy, and larger doses are recommended for surgical prophylaxis in pregnant women to obtain the same antibacterial effect as in nonpregnant patients. Cefazolin has a longer half-life in neonates than in adults. Maternal administration of up to 2 g of cefazolin is effective and produces exposure within clinically approved limits in neonates.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Nishida M, Matsubara T, Murakawa T, Mine Y, Yokota Y, Kuwahara S, Goto S. 1969. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of cefazolin, a new cephalosporin C derivative. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 9:236–243 - PubMed
-
- Sullivan SA, Smith T, Chang E, Hulsey T, Vandorsten JP, Soper D. 2007. Administration of cefazolin prior to skin incision is superior to cefazolin at cord clamping in preventing postcesarean infectious morbidity: a randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 196:455.e1–455.e5 (Erratum, 197:333, 2007.) 10.1016/j.ajog.2007.03.022 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beal SL, Sheiner LB, Boeckmann AJ. 1994. NONMEM user's guides - Part V. NONMEM Project Group, University of California at San Francisco, San Francisco, CA
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

