Trends in cardiovascular disease risk factors by obesity level in adults in the United States, NHANES 1999-2010
- PMID: 24733690
- PMCID: PMC4560453
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.20761
Trends in cardiovascular disease risk factors by obesity level in adults in the United States, NHANES 1999-2010
Abstract
Objective: To assess whether trends in cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors by among overweight and obese US adults have improved.
Methods: The study included 10,568 adults 18 years and older who participated in National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999-2010. CVD risk factors included diabetes (self-reported diagnosis, glycated hemoglobin ≥6.5%, or fasting plasma glucose ≥126mg/dl), hypertension (treatment or blood pressure ≥140/90 mmHg), dyslipidemia (treatment or non-HDL cholesterol ≥160 mg/dl), and smoking (self-report or cotinine levels ≥10 ng/ml). The prevalence and temporal trends of CVD risk factors for each BMI group were estimated.
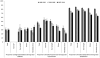
Results: In 2007-2010, the prevalence of diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia was highest among obese (18.5%, 35.7%, 49.7%, respectively) followed by overweight (8.2%, 26.4%, 44.2%, respectively) and normal weight adults (5.4%, 19.8%, 28.6%, respectively). Smoking exposure was highest among normal weight (29.8%) followed by overweight (24.8%) and obese adults (24.6%). From 1999-2002 to 2007-2010, untreated hypertension decreased among obese and overweight adults and untreated dyslipidemia decreased for all weight groups. There were no significant temporal changes in smoking across BMI groups.
Conclusions: Despite decreases in untreated risk factors, it is important to improve the CVD risk profile of overweight and obese US adults.
Keywords: NHANES; adults; cardiovascular disease risk factors; diabetes; dyslipidemia; hypertension; obesity.
Copyright © 2014 The Obesity Society. This article is a US government work and, as such, is in the public domain in the United States of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999-2010. JAMA. 2012;307:491–497. - PubMed
-
- Brown CD, Higgins M, Donato KA, Rohde FC, Garrison R, Obarzanek E, et al. Body mass index and the prevalence of hypertension and dyslipidemia. Obes Res. 2000;8:605–619. - PubMed
-
- Wilson PW, D'Agostino RB, Sullivan L, Parise H, Kannel WB. Overweight and obesity as determinants of cardiovascular risk: the Framingham experience. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:1867–1872. - PubMed
-
- Abdullah A, Peeters A, de Courten M, Stoelwinder J. The magnitude of association between overweight and obesity and the risk of diabetes: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;89:309–319. - PubMed
-
- Peeters A, Backholer K. Is the health burden associated with obesity changing? Am J Epidemiol. 2012;176:840–845. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

