X-ray structure of human aquaporin 2 and its implications for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus and trafficking
- PMID: 24733887
- PMCID: PMC4035913
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1321406111
X-ray structure of human aquaporin 2 and its implications for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus and trafficking
Abstract
Human aquaporin 2 (AQP2) is a water channel found in the kidney collecting duct, where it plays a key role in concentrating urine. Water reabsorption is regulated by AQP2 trafficking between intracellular storage vesicles and the apical membrane. This process is tightly controlled by the pituitary hormone arginine vasopressin and defective trafficking results in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI). Here we present the X-ray structure of human AQP2 at 2.75 Å resolution. The C terminus of AQP2 displays multiple conformations with the C-terminal α-helix of one protomer interacting with the cytoplasmic surface of a symmetry-related AQP2 molecule, suggesting potential protein-protein interactions involved in cellular sorting of AQP2. Two Cd(2+)-ion binding sites are observed within the AQP2 tetramer, inducing a rearrangement of loop D, which facilitates this interaction. The locations of several NDI-causing mutations can be observed in the AQP2 structure, primarily situated within transmembrane domains and the majority of which cause misfolding and ER retention. These observations provide a framework for understanding why mutations in AQP2 cause NDI as well as structural insights into AQP2 interactions that may govern its trafficking.
Keywords: X-ray crystallography; membrane protein; water channel protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

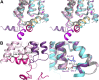


References
-
- Verbalis JG. Disorders of body water homeostasis. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;17(4):471–503. - PubMed
-
- van Os CH, Deen PM, Dempster JA. Aquaporins: Water selective channels in biological membranes. Molecular structure and tissue distribution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1197(3):291–309. - PubMed
-
- Noda Y, Sohara E, Ohta E, Sasaki S. Aquaporins in kidney pathophysiology. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010;6(3):168–178. - PubMed
-
- Fushimi K, Sasaki S, Marumo F. Phosphorylation of serine 256 is required for cAMP-dependent regulatory exocytosis of the aquaporin-2 water channel. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(23):14800–14804. - PubMed
-
- Katsura T, Gustafson CE, Ausiello DA, Brown D. Protein kinase A phosphorylation is involved in regulated exocytosis of aquaporin-2 in transfected LLC-PK1 cells. Am J Physiol. 1997;272(6 Pt 2):F817–F822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

