Gq/5-HT2c receptor signals activate a local GABAergic inhibitory feedback circuit to modulate serotonergic firing and anxiety in mice
- PMID: 24733892
- PMCID: PMC4035925
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1321576111
Gq/5-HT2c receptor signals activate a local GABAergic inhibitory feedback circuit to modulate serotonergic firing and anxiety in mice
Abstract
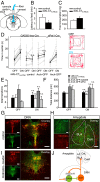
Serotonin 2c receptors (5-HT2c-Rs) are drug targets for certain mental disorders, including schizophrenia, depression, and anxiety. 5-HT2c-Rs are expressed throughout the brain, making it difficult to link behavioral changes to circuit specific receptor expression. Various 5-HT-Rs, including 5-HT2c-Rs, are found in the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN); however, the function of 5-HT2c-Rs and their influence on the serotonergic signals mediating mood disorders remain unclear. To investigate the role of 5-HT2c-Rs in the DRN in mice, we developed a melanopsin-based optogenetic probe for activation of Gq signals in cellular domains, where 5-HT2c-Rs are localized. Our results demonstrate that precise temporal control of Gq signals in 5-HT2c-R domains in GABAergic neurons upstream of 5-HT neurons provides negative feedback regulation of serotonergic firing to modulate anxiety-like behavior in mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lowry CA, Johnson PL, Hay-Schmidt A, Mikkelsen J, Shekhar A. Modulation of anxiety circuits by serotonergic systems. Stress. 2005;8(4):233–246. - PubMed
-
- Barnes NM, Sharp T. A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38(8):1083–1152. - PubMed
-
- Millan MJ. Serotonin 5-HT2C receptors as a target for the treatment of depressive and anxious states: Focus on novel therapeutic strategies. Therapie. 2005;60(5):441–460. - PubMed
-
- Sharp T, Boothman L, Raley J, Quérée P. Important messages in the “post”: Recent discoveries in 5-HT neurone feedback control. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007;28(12):629–636. - PubMed
-
- Sanders-Bush E, Burris KD, Knoth K. Lysergic acid diethylamide and 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine are partial agonists at serotonin receptors linked to phosphoinositide hydrolysis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988;246(3):924–928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

