Structural basis for regulation of rhizobial nodulation and symbiosis gene expression by the regulatory protein NolR
- PMID: 24733893
- PMCID: PMC4035926
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1402243111
Structural basis for regulation of rhizobial nodulation and symbiosis gene expression by the regulatory protein NolR
Abstract
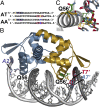
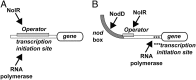
The symbiosis between rhizobial microbes and host plants involves the coordinated expression of multiple genes, which leads to nodule formation and nitrogen fixation. As part of the transcriptional machinery for nodulation and symbiosis across a range of Rhizobium, NolR serves as a global regulatory protein. Here, we present the X-ray crystal structures of NolR in the unliganded form and complexed with two different 22-base pair (bp) double-stranded operator sequences (oligos AT and AA). Structural and biochemical analysis of NolR reveals protein-DNA interactions with an asymmetric operator site and defines a mechanism for conformational switching of a key residue (Gln56) to accommodate variation in target DNA sequences from diverse rhizobial genes for nodulation and symbiosis. This conformational switching alters the energetic contributions to DNA binding without changes in affinity for the target sequence. Two possible models for the role of NolR in the regulation of different nodulation and symbiosis genes are proposed. To our knowledge, these studies provide the first structural insight on the regulation of genes involved in the agriculturally and ecologically important symbiosis of microbes and plants that leads to nodule formation and nitrogen fixation.
Keywords: protein structure; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Desbrosses GJ, Stougaard J. Root nodulation: A paradigm for how plant-microbe symbiosis influences host developmental pathways. Cell Host Microbe. 2011;10(4):348–358. - PubMed
-
- Kondorosi E, Mergaert P, Kereszt A. A paradigm for endosymbiotic life: Cell differentiation of Rhizobium bacteria provoked by host plant factors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2013;67:611–628. - PubMed
-
- Masson-Boivin C, Giraud E, Perret X, Batut J. Establishing nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with legumes: How many rhizobium recipes? Trends Microbiol. 2009;17(10):458–466. - PubMed
-
- Horvath B, et al. Organization, structure and symbiotic function of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes determining host specificity for alfalfa. Cell. 1986;46(3):335–343. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

