Comparison of BMI, AHI, and apolipoprotein E ε4 (APOE-ε4) alleles among sleep apnea patients with different skeletal classifications
- PMID: 24733985
- PMCID: PMC3960382
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.3614
Comparison of BMI, AHI, and apolipoprotein E ε4 (APOE-ε4) alleles among sleep apnea patients with different skeletal classifications
Abstract
Study objectives: This case-control study investigated whether variations within the APOE-ε gene were associated with having a convex facial profile (skeletal Class II) compared to exhibiting a straight or concave facial profile (Class I or Class III) among patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Associations between the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) and body mass index (BMI) scores for these OSA patients were also examined in the context of facial profile.
Method: OSA patients with an AHI ≥ 15 were recruited from a sleep clinic and classified by facial and dental occlusal relationships based on a profile facial analysis, lateral photographs, and dental examination. Saliva was collected as a source of DNA. The APOE-ε1-4 allele-defining single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) rs429358 and rs7412 were genotyped. A χ(2) analysis was used to assess Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and for association analysis (significance at p < 0.05). ANOVA and Fisher exact test were also used.
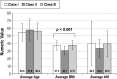
Result: Seventy-six Caucasian OSA patients participated in the study-25 Class II cases and 51 non-Class II cases. There was no association of the APOE-ε4 allele with facial profile among these OSA patients. Class II OSA patients had significantly lower BMIs (30.7 ± 5.78) than Class I (37.3 ± 6.14) or Class III (37.8 ± 6.17) patients (p < 0.001), although there was no statistical difference in AHI for Class II patients compared with other groups.
Conclusion: OSA patients with Class II convex profile were more likely to have a lower BMI than those in other skeletal groups. In fact 20% of them were not obese, suggesting that a Class II convex profile may influence or be associated with OSA development independent of BMI.
Keywords: AHI; APOE-ε; BMI; Obstructive sleep apnea; facial profile; skeletal malocclusion.
Figures
References
-
- Albajalan OB, Samsudin AR, Hassan R. Craniofacial morphology of Malay patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur J Orthod. 2011;33:509–14. - PubMed
-
- Chokroverty S. Overview of sleep & sleep disorders. Indian J Med Res. 2010;131:126–40. - PubMed
-
- Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:1217–39. - PubMed
-
- Miyao E, Noda A, Miyao M, Yasuma F, Inafuku S. The role of malocclusion in non-obese patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Intern Med. 2008;47:1573–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous