Feasibility of endoscopic treatment of middle ear myoclonus: a cadaveric study
- PMID: 24734199
- PMCID: PMC3964766
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/175268
Feasibility of endoscopic treatment of middle ear myoclonus: a cadaveric study
Abstract
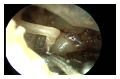
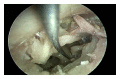
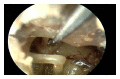
Stapedius and tensor tympani tenotomy is a relatively simple surgical procedure commonly performed to control pulsatile tinnitus due to middle ear myoclonus and for several other indications. We designed a cadaveric study to assess the feasibility of an entirely endoscopic approach to stapedius and tensor tympani tenotomy. We performed this endoscopic ear surgery in 10 cadaveric temporal bones and summarized our experience. Endoscopic stapedius and tensor tympani section is a new, minimally invasive treatment option for middle ear myoclonus that should be considered as the first line surgical approach in patients who fail medical therapy. The use of an endoscopic approach allows for easier access and vastly superior visualization of the relevant anatomy, which in turn allows the surgeon to minimize tissue dissection. The entire operation, including raising the tympanomeatal flap and tendon section, can be safely completed under visualization with a rigid endoscope.
Figures



References
-
- Bhimrao SK, Masterson L, Baguley D. Systematic review of management strategies for middle ear myoclonus. Otolaryngology. 2012;146:698–706. - PubMed
-
- Hidaka H, Honkura Y, Ota J, et al. Middle ear myoclonus cured by selective tenotomy of the tensor tympani: strategies for targeted intervention for middle ear muscles. Otology and Neurotology. 2013;34:1552–1558. - PubMed
-
- Zipfel TE, Kaza SR, Greene JS. Middle-ear myoclonus. Journal of Laryngology and Otology. 2000;114(3):207–209. - PubMed
-
- Park SN, Bae SC, Lee GH, et al. Clinical characteristics and therapeutic response of objective tinnitus due to middle ear myoclonus: a large case series. Laryngoscope. 2013;123:2516–2520. - PubMed
-
- Badia L, Parikh A, Brookes GB. Management of middle ear myoclonus. Journal of Laryngology and Otology. 1994;108(5):380–382. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

