Neural mechanisms of self-location
- PMID: 24735859
- PMCID: PMC3995086
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.02.049
Neural mechanisms of self-location
Abstract
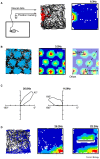
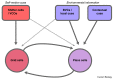
The ability to self-localise and to navigate to remembered goals in complex and changeable environments is crucial to the survival of many mobile species. Electrophysiological investigations of the mammalian hippocampus and associated brain structures have identified several classes of neurons which represent information about an organism's position and orientation. These include place cells, grid cells, head direction cells, and boundary vector cells, as well as cells representing aspects of self-motion. Understanding how these neural representations are formed and updated from environmental sensory information and from information relating to self-motion is an important topic attracting considerable current interest. Here we review the computational mechanisms thought to underlie the formation of these different spatial representations, the interactions between them, and their use in guiding behaviour. These include some of the clearest examples of computational mechanisms of general interest to neuroscience, such as attractor dynamics, temporal coding and multi-modal integration. We also discuss the close relationships between computational modelling and experimental research which are driving progress in this area.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Darwin C. Origin of certain instincts. Nature. 1873;7:417–418.
-
- O’Keefe J., Dostrovsky J. The hippocampus as a spatial map. Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat. Brain Res. 1971;34:171–175. - PubMed
-
- Ranck Head-direction cells in the deep layers of the dorsal presubiculum in freely moving rats. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 1984;10:599.
-
- Hafting T., Fyhn M., Molden S., Moser M.-B., Moser E.I. Microstructure of a spatial map in the entorhinal cortex. Nature. 2005;436:801–806. - PubMed
-
- Wilson M.A., McNaughton B.L. Dynamics of the hippocampal code for space. Science. 1993;261:1055–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

