Hepatic mitochondrial and ER stress induced by defective PPARα signaling in the pathogenesis of hepatic steatosis
- PMID: 24735884
- PMCID: PMC4280162
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00438.2013
Hepatic mitochondrial and ER stress induced by defective PPARα signaling in the pathogenesis of hepatic steatosis
Abstract
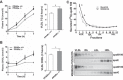
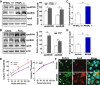
Emerging evidence demonstrates a close interplay between disturbances in mitochondrial function and ER homeostasis in the development of the metabolic syndrome. The present investigation sought to advance our understanding of the communication between mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress in the onset of hepatic steatosis in male rodents with defective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPARα) signaling. Genetic depletion of PPARα or perturbation of PPARα signaling by high-fructose diet compromised the functional activity of metabolic enzymes involved in mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation and induced hepatic mitochondrial stress in rats and mice. Inhibition of PPARα activity further enhanced the expression of apolipoprotein B (apoB) mRNA and protein, which was associated with reduced mRNA expression of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (SERCA), the induction of hepatic ER stress, and hepatic steatosis. Restoration of PPARα activity recovered the metabolic function of the mitochondria and ER, alleviated systemic hypertriglyceridemia, and improved hepatic steatosis. These findings unveil novel roles for PPARα in mediating stress signals between hepatic subcellular stress-responding machinery and in the onset of hepatic steatosis under conditions of metabolic stress.
Keywords: apolipoprotein B; endoplasmic reticulum; hepatic steatosis; mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum stress; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α; very-low density lipoprotein.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures




References
-
- Aoyama T, Peters JM, Iritani N, Nakajima T, Furihata K, Hashimoto T, Gonzalez FJ. Altered constitutive expression of fatty acid-metabolizing enzymes in mice lacking the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha). J Biol Chem 273: 5678–5684, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Basciano H, Miller AE, Naples M, Baker C, Kohen R, Xu E, Su Q, Allister EM, Wheeler MB, Adeli K. Metabolic effects of dietary cholesterol in an animal model of insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297: E462–E473, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Bensinger SJ, Tontonoz P. Integration of metabolism and inflammation by lipid-activated nuclear receptors. Nature 454: 470–477, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Bernal-Mizrachi C, Weng S, Feng C, Finck BN, Knutsen RH, Leone TC, Coleman T, Mecham RP, Kelly DP, Semenkovich CF. Dexamethasone induction of hypertension and diabetes is PPAR-alpha dependent in LDL receptor-null mice. Nat Med 9: 1069–1075, 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

