Predicting sleep disordered breathing in outpatients with suspected OSA
- PMID: 24736037
- PMCID: PMC4010842
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-004519
Predicting sleep disordered breathing in outpatients with suspected OSA
Abstract
Objective: To validate the utilities of Berlin, STOP and STOP-BANG Questionnaires, other patient characteristics, comorbidities, Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS), fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO) and blood markers for the prediction of sleep disordered breathing (SDB) on limited polygraphy.
Setting: North Glasgow Sleep Service (a tertiary referral centre).
Participants: 129 consecutive patients, aged ≥16 years, referred to the sleep clinic for assessment of possible obstructive sleep apnoea.
Interventions: We selected cut-points of apnoea hypopnoea index (AHI) of ≥5 and ≥15/h from their home polygraphy and determined associations of these with individual symptoms, questionnaire scores and other results. Receiver operating characteristic analysis and univariate and multivariate logistic regression were used to explore these.
Primary and secondary outcomes measures: Primary: The utility of STOP, STOP-BANG and Berlin Questionnaires for prediction of SDB. Secondary: The utility of other measures for prediction of SDB.
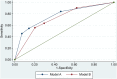
Results: AHI was ≥5 in 97 patients and ≥15 in 56 patients. STOP and STOP-BANG scores were associated with both AHI cut-points but results with ESS and Berlin Questionnaire scores were negative. STOP-BANG had a negative predictive value 1.00 (0.77-1.00) for an AHI ≥15 with a score ≥3 predicting AHI ≥5 with sensitivity 0.93 (95% CI 0.84 to 0.98) and accuracy 79%, while a score ≥6 predicted AHI ≥15 with specificity 0.78 (0.65 to 0.88) and accuracy 72%. Neck circumference ≥17 inch and presence of witnessed apnoeas were independent predictors of SDB.
Conclusions: STOP and STOP-BANG Questionnaires have utility for the prediction of SDB in the sleep clinic population. Modification of the STOP-BANG Questionnaire merits further study in this and other patient groups.
Keywords: SLEEP MEDICINE.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sleep-disordered breathing in patients with cardiovascular diseases cannot be detected by ESS, STOP-BANG, and Berlin questionnaires.Clin Res Cardiol. 2018 Nov;107(11):1071-1078. doi: 10.1007/s00392-018-1282-7. Epub 2018 May 29. Clin Res Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29845331
-
Application value of the NoSAS score for screening sleep-disordered breathing.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Aug;10(8):4774-4781. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.07.46. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30233849 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of patients with sleep disordered breathing: comparing the four-variable screening tool, STOP, STOP-Bang, and Epworth Sleepiness Scales.J Clin Sleep Med. 2011 Oct 15;7(5):467-72. doi: 10.5664/JCSM.1308. J Clin Sleep Med. 2011. PMID: 22003341 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of the Berlin questionnaire, STOP-BANG, STOP, and Epworth sleepiness scale in detecting obstructive sleep apnea: A bivariate meta-analysis.Sleep Med Rev. 2017 Dec;36:57-70. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Sleep Med Rev. 2017. PMID: 27919588 Review.
-
Validation of the STOP-Bang questionnaire as a screening tool for obstructive sleep apnoea in patients with cardiovascular risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2021 Mar;8(1):e000848. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2020-000848. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 33664122 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
BASAN index (Body mass index, Age, Sex, Arterial hypertension and Neck circumference) predicts severe apnoea in adults living at high altitude.BMJ Open. 2021 Jun 24;11(6):e044228. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044228. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34168022 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline.J Clin Sleep Med. 2017 Mar 15;13(3):479-504. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.6506. J Clin Sleep Med. 2017. PMID: 28162150 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of exhaled nitric oxide concentration in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Mar;96(12):e6429. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006429. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28328850 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the GOAL Questionnaire as an Obstructive Sleep Apnea Screening Instrument in Bariatric Surgery Candidates: a Brazilian Single-Center Study.Obes Surg. 2020 Dec;30(12):4802-4809. doi: 10.1007/s11695-020-04888-4. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Obes Surg. 2020. PMID: 32748204
-
Twenty-four hour Blood Pressure in Obese Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2017 Oct;109(4):313-320. doi: 10.5935/abc.20170130. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28876375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, et al. The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med 1993;328:1230–5 - PubMed
-
- McNicholas WT. Diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2008;5:154–60 - PubMed
-
- Lacasse Y, Godbout C, Series F. Health-related quality of life in obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J 2002;19:499–503 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
