Targeted disruption of β-arrestin 2-mediated signaling pathways by aptamer chimeras leads to inhibition of leukemic cell growth
- PMID: 24736311
- PMCID: PMC3988186
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093441
Targeted disruption of β-arrestin 2-mediated signaling pathways by aptamer chimeras leads to inhibition of leukemic cell growth
Abstract
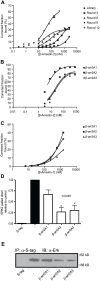
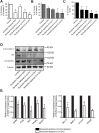
β-arrestins, ubiquitous cellular scaffolding proteins that act as signaling mediators of numerous critical cellular pathways, are attractive therapeutic targets because they promote tumorigenesis in several tumor models. However, targeting scaffolding proteins with traditional small molecule drugs has been challenging. Inhibition of β-arrestin 2 with a novel aptamer impedes multiple oncogenic signaling pathways simultaneously. Additionally, delivery of the β-arrestin 2-targeting aptamer into leukemia cells through coupling to a recently described cancer cell-specific delivery aptamer, inhibits multiple β-arrestin-mediated signaling pathways known to be required for chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) disease progression, and impairs tumorigenic growth in CML patient samples. The ability to target scaffolding proteins such as β-arrestin 2 with RNA aptamers may prove beneficial as a therapeutic strategy.
Highlights: An RNA aptamer inhibits β-arrestin 2 activity.Inhibiting β-arrestin 2 impedes multiple tumorigenic pathways simultaneously.The therapeutic aptamer is delivered to cancer cells using a cell-specific DNA aptamer.Targeting β-arrestin 2 inhibits tumor progression in CML models and patient samples.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Glucocorticoids regulate arrestin gene expression and redirect the signaling profile of G protein-coupled receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 23;109(43):17591-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1209411109. Epub 2012 Oct 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23045642 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-arrestin links endothelin A receptor to beta-catenin signaling to induce ovarian cancer cell invasion and metastasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Feb 24;106(8):2806-11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807158106. Epub 2009 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19202075 Free PMC article.
-
β-Arrestin signal complex plays a critical role in adipose differentiation.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Jul;45(7):1281-92. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.03.014. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23557604
-
Beta-arrestin signaling and regulation of transcription.J Cell Sci. 2007 Jan 15;120(Pt 2):213-8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03338. J Cell Sci. 2007. PMID: 17215450 Review.
-
β-arrestin-mediated signaling improves the efficacy of therapeutics.J Pharmacol Sci. 2012;118(4):408-12. doi: 10.1254/jphs.11r10cp. Epub 2012 Mar 23. J Pharmacol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22447307 Review.
Cited by
-
Aptamer-based approaches in leukemia: a paradigm shift in targeted therapy.Clin Exp Med. 2025 May 30;25(1):186. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01724-w. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40445231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Aptamer-Protein Interactions.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022 Nov 4;5(12):1211-1227. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.2c00156. eCollection 2022 Dec 9. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 36524009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Aptamer That Rapidly Internalizes into Cancer Cells Utilizes the Transferrin Receptor Pathway.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 14;15(8):2301. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082301. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190227 Free PMC article.
-
Oligonucleotide Aptamer-Mediated Precision Therapy of Hematological Malignancies.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018 Dec 7;13:164-175. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.08.023. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018. PMID: 30292138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilization of Biased G Protein-Coupled ReceptorSignaling towards Development of Safer andPersonalized Therapeutics.Molecules. 2019 May 29;24(11):2052. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112052. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31146474 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeWire SM, Ahn S, Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK (2007) Beta-arrestins and cell signaling. Annu Rev Physiol 69, 483–510 - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Ferguson SS, Barak LS, Aber MJ, Giros B, et al. (1997) Molecular mechanisms of G protein-coupled receptor signaling: role of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and arrestins in receptor desensitization and resensitization. Receptors Channels 5, 193–199 - PubMed
-
- Lin FT, Daaka Y, Lefkowitz RJ (1998) beta-arrestins regulate mitogenic signaling and clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. The Journal of biological chemistry 273, 31640–31643 - PubMed
-
- Luttrell LM, Ferguson SS, Daaka Y, Miller WE, Maudsley S, et al. (1999) Beta-arrestin-dependent formation of beta2 adrenergic receptor-Src protein kinase complexes. Science 283, 655–661 - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Ren XR, Nelson CD, Barak LS, Chen JK, et al. (2004) Activity-dependent internalization of smoothened mediated by beta-arrestin 2 and GRK2. Science 306, 2257–2260 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

