Targeted disruption of β-arrestin 2-mediated signaling pathways by aptamer chimeras leads to inhibition of leukemic cell growth
- PMID: 24736311
- PMCID: PMC3988186
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093441
Targeted disruption of β-arrestin 2-mediated signaling pathways by aptamer chimeras leads to inhibition of leukemic cell growth
Abstract
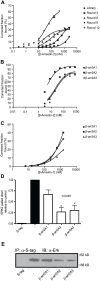
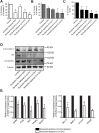
β-arrestins, ubiquitous cellular scaffolding proteins that act as signaling mediators of numerous critical cellular pathways, are attractive therapeutic targets because they promote tumorigenesis in several tumor models. However, targeting scaffolding proteins with traditional small molecule drugs has been challenging. Inhibition of β-arrestin 2 with a novel aptamer impedes multiple oncogenic signaling pathways simultaneously. Additionally, delivery of the β-arrestin 2-targeting aptamer into leukemia cells through coupling to a recently described cancer cell-specific delivery aptamer, inhibits multiple β-arrestin-mediated signaling pathways known to be required for chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) disease progression, and impairs tumorigenic growth in CML patient samples. The ability to target scaffolding proteins such as β-arrestin 2 with RNA aptamers may prove beneficial as a therapeutic strategy.
Highlights: An RNA aptamer inhibits β-arrestin 2 activity.Inhibiting β-arrestin 2 impedes multiple tumorigenic pathways simultaneously.The therapeutic aptamer is delivered to cancer cells using a cell-specific DNA aptamer.Targeting β-arrestin 2 inhibits tumor progression in CML models and patient samples.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- DeWire SM, Ahn S, Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK (2007) Beta-arrestins and cell signaling. Annu Rev Physiol 69, 483–510 - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Ferguson SS, Barak LS, Aber MJ, Giros B, et al. (1997) Molecular mechanisms of G protein-coupled receptor signaling: role of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and arrestins in receptor desensitization and resensitization. Receptors Channels 5, 193–199 - PubMed
-
- Lin FT, Daaka Y, Lefkowitz RJ (1998) beta-arrestins regulate mitogenic signaling and clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. The Journal of biological chemistry 273, 31640–31643 - PubMed
-
- Luttrell LM, Ferguson SS, Daaka Y, Miller WE, Maudsley S, et al. (1999) Beta-arrestin-dependent formation of beta2 adrenergic receptor-Src protein kinase complexes. Science 283, 655–661 - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Ren XR, Nelson CD, Barak LS, Chen JK, et al. (2004) Activity-dependent internalization of smoothened mediated by beta-arrestin 2 and GRK2. Science 306, 2257–2260 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

