MHC-I expression renders catecholaminergic neurons susceptible to T-cell-mediated degeneration
- PMID: 24736453
- PMCID: PMC4024461
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4633
MHC-I expression renders catecholaminergic neurons susceptible to T-cell-mediated degeneration
Abstract
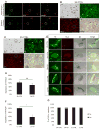
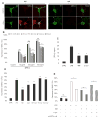
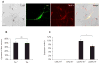
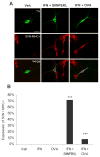
Subsets of rodent neurons are reported to express major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I), but such expression has not been reported in normal adult human neurons. Here we provide evidence from immunolabel, RNA expression and mass spectrometry analysis of postmortem samples that human catecholaminergic substantia nigra and locus coeruleus neurons express MHC-I, and that this molecule is inducible in human stem cell-derived dopamine (DA) neurons. Catecholamine murine cultured neurons are more responsive to induction of MHC-I by gamma-interferon than other neuronal populations. Neuronal MHC-I is also induced by factors released from microglia activated by neuromelanin or alpha-synuclein, or high cytosolic DA and/or oxidative stress. DA neurons internalize foreign ovalbumin and display antigen derived from this protein by MHC-I, which triggers DA neuronal death in the presence of appropriate cytotoxic T cells. Thus, neuronal MHC-I can trigger antigenic response, and catecholamine neurons may be particularly susceptible to T-cell-mediated cytotoxic attack.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Wong GH, Bartlett PF, Clark-Lewis I, Battye F, Schrader JW. Inducible expression of H-2 and Ia antigens on brain cells. Nature. 1984;310:688–91. - PubMed
-
- Neumann H, Cavalié A, Jenne DE, Wekerle H. Induction of MHC class I genes in neurons. Science. 1995;28, 269(5223):549–52. - PubMed
-
- Lindå H, Hammarberg H, Piehl F, Khademi M, Olsson T. Expression of MHC class I and beta2-microglobulin in rat spinal motoneurons: regulatory influences by IFN-gamma and axotomy. Exp Neurol. 1999;150:282–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

