The HIV matrix protein p17 promotes the activation of human hepatic stellate cells through interactions with CXCR2 and Syndecan-2
- PMID: 24736615
- PMCID: PMC3988079
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094798
The HIV matrix protein p17 promotes the activation of human hepatic stellate cells through interactions with CXCR2 and Syndecan-2
Abstract
Background: The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) p17 is a matrix protein involved in virus life's cycle. CXCR2 and Syndecan-2, the two major coreceptors for the p17 protein, are expressed in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), a key cell type involved in matrix deposition in liver fibrotic disorders.
Aim: In this report we have investigated the in vitro impact of p17 on HSCs transdifferentiation and function and underlying signaling pathways involved in these processes.
Methods: LX-2 cells, a human HSC line, and primary HSC were challenged with p17 and expressions of fibrogenic markers and of p17 receptors were assessed by qRT-PCR and Western blot. Downstream intracellular signaling pathways were evaluated with qRT-PCR and Western blot as well as after pre-treatment with specific pathway inhibitors.
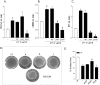
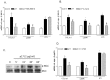
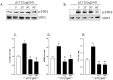
Results: Exposure of LX2 cells to p17 increases their contractile force, reshapes the cytoskeleton fibers and upregulates the expression of transdifferentiation markers including αSMA, COL1α1 and endothelin-1 through the activation of Jak/STAT and Rho signaling pathways. These effects are lost in HSCs pre-incubated with a serum from HIV positive person who underwent a vaccination with a p17 peptide. Confocal laser microscopy studies demonstrates that CXCR2 and syndecan-2 co-associate at the plasma membrane after exposure to p17. Immunostaining of HIV/HCV liver biopsies from co-infected patients reveals that the progression of liver fibrosis correlates with a reduced expression of CXCR2.
Conclusions: The HIV matrix protein p17 is pro-fibrogenic through its interactions both with CXCR2 and syndecan-2 on activated HSCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
X4 Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 promotes human hepatic stellate cell activation and collagen I expression through interactions with CXCR4.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033659. Epub 2012 Mar 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479424 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 p17 matrix protein interacts with heparan sulfate side chain of CD44v3, syndecan-2, and syndecan-4 proteoglycans expressed on human activated CD4+ T cells affecting tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 2 production.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 3;286(22):19541-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.191270. Epub 2011 Apr 11. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21482826 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 matrix protein p17 promotes lymphangiogenesis and activates the endothelin-1/endothelin B receptor axis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Apr;34(4):846-56. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302478. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24482377
-
HIV-1 Matrix Protein p17 and its Receptors.Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(1):23-32. doi: 10.2174/1389450116666150825110840. Curr Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26302809 Review.
-
Stellate cell contraction: role, regulation, and potential therapeutic target.Clin Liver Dis. 2008 Nov;12(4):791-803, viii. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2008.07.004. Clin Liver Dis. 2008. PMID: 18984467 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HIV-1 Structural Proteins Serve as PAMPs for TLR2 Heterodimers Significantly Increasing Infection and Innate Immune Activation.Front Immunol. 2015 Aug 19;6:426. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00426. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26347747 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling HIV1-host protein-protein interaction networks in patient-derived exosome proteins: impact on pathophysiology and innate immune pathways.Virol J. 2025 Jul 28;22(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02717-7. Virol J. 2025. PMID: 40722180 Free PMC article.
-
The HIV matrix protein p17 induces hepatic lipid accumulation via modulation of nuclear receptor transcriptoma.Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 15;5:15403. doi: 10.1038/srep15403. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26469385 Free PMC article.
-
The role of liver macrophages in viral liver pathogenesis.J Leukoc Biol. 2025 Sep 1;117(9):qiaf088. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiaf088. J Leukoc Biol. 2025. PMID: 40561105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coreceptor functions of cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 May 1;322(5):C896-C912. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00050.2022. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35319900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sulkowski MS (2008) Management of hepatic complications in HIV-infected persons. J Infect Dis 197: S279e93. - PubMed
-
- Weber R, Sabin CA, Friis-Moller N, Reiss P, El-Sadr WM, et al. (2006) Liver related deaths in persons infected with the human immunodeficiency virus: the D:A:D study. Arch Intern Med 166: 1632e41. - PubMed
-
- Bongiovanni M, Tordato F (2007) Steatohepatitis in HIV infected subjects: pathogenesis, clinical impact and implications in clinical management. Curr HIV Res 5: 490e8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

