Acute coronary syndrome remodels the protein cargo and functions of high-density lipoprotein subfractions
- PMID: 24736723
- PMCID: PMC3988065
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094264
Acute coronary syndrome remodels the protein cargo and functions of high-density lipoprotein subfractions
Abstract
Objectives: This study examined alterations in the functions and proteome of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) subfractions (HDL2 and HDL3) isolated from patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) compared with control subjects.
Methods: We measured HDL subfraction cholesterol efflux capacity, inflammatory index (HII), paraoxonase-1 (PON1) activity, and lipid hydroperoxide (LOOH) levels in both male age-matched controls and the ACS group (n = 40/group). Additionally, proteomic analysis was used to monitor changes in the HDL subfraction proteome between controls and ACS subjects.
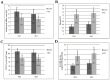
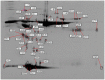
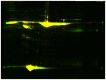
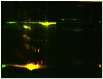
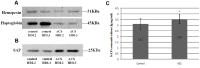
Results: Both HDL2 and HDL3 from ACS patients had greater HII and LOOH levels compared with controls (P<0.001); PON1 activity and cholesterol efflux capacity in both HDL2 and HDL3 from the ACS group were significantly less than those of controls (P<0.001). Using proteomic analysis, we demonstrated that, compared with the control group, nine proteins were selectively enriched in HDL3 from subjects with ACS, and ras-related protein Rab-7b was decreased in HDL3. Additionally, in the ACS subjects, 12 proteins were decreased in HDL2 and 4 proteins were increased in HDL2.
Conclusions: Functional HDL subfractions shifted to dysfunctional HDL subfractions during ACS, and the functional impairment was linked to remodeled protein cargo in HDL subfractions from ACS patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gordon DJ, Probstfield JL, Garrison RJ, Neaton JD, Castelli WP, et al. (1989) High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. Four prospective American studies. Circulation 79: 8–15. - PubMed
-
- Duffy D, Rader DJ (2009) Update on strategies to increase HDL quantity and function. Nature Reviews Cardiology 6: 455–63. - PubMed
-
- Guo ZG, Li C, Zhong JK, Tu Y, Xie D (2012) Laboratory investigation of dysfunctional HDL. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 165: 32–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

