Combination of hypomorphic mutations of the Drosophila homologues of aryl hydrocarbon receptor and nucleosome assembly protein family genes disrupts morphogenesis, memory and detoxification
- PMID: 24736732
- PMCID: PMC3988104
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0094975
Combination of hypomorphic mutations of the Drosophila homologues of aryl hydrocarbon receptor and nucleosome assembly protein family genes disrupts morphogenesis, memory and detoxification
Abstract
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor is essential for biological responses to endogenous and exogenous toxins in mammals. Its Drosophila homolog spineless plays an important role in fly morphogenesis. We have previously shown that during morphogenesis spineless genetically interacts with CG5017 gene, which encodes a nucleosome assembly factor and may affect cognitive function of the fly. We now demonstrate synergistic interactions of spineless and CG5017 in pathways controlling oxidative stress response and long-term memory formation in Drosophila melanogaster. Oxidative stress was induced by low doses of X-ray irradiation of flies carrying hypomorphic mutation of spineless, mutation of CG5017, and their combination. To determine the sensitivity of these mutants to pharmacological modifiers of the irradiation effect, we irradiated flies growing on standard medium supplemented by radiosensitizer furazidin and radioprotector serotonin. The effects of irradiation were investigated by analyzing leg and antenna morphological structures and by using real-time PCR to measure mRNA expression levels for spineless, Cyp6g1 and Gst-theta genes. We also examined long-term memory in these mutants using conditioned courtship suppression paradigm. Our results show that the interaction of spineless and CG5017 is important for regulation of morphogenesis, long-term memory formation, and detoxification during oxidative stress. Since spineless and CG5017 are evolutionary conserved, these results must be considered when evaluating the risk of combining similar mutations in other organisms, including humans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

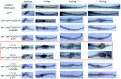
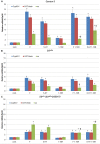
 - P<0.05, compared to F or 5-HT group.
- P<0.05, compared to F or 5-HT group.
 of tested males. (B, D, F, H) –
of tested males. (B, D, F, H) –  of tested males. On the X-axis: time following training, in days; on the Y axis:
of tested males. On the X-axis: time following training, in days; on the Y axis:  – courtship index,
– courtship index,  – learning index, standard units. Open columns –
– learning index, standard units. Open columns –  of naive males, hatched columns –
of naive males, hatched columns –  (
( ) of trained males. Each point represents 20 males. ** -
) of trained males. Each point represents 20 males. ** -  or
or  significantly lower than for wild type (two-sided randomization test,
significantly lower than for wild type (two-sided randomization test,  ) in similar condition;
) in similar condition;  -
-  in a test immediately following training or in a deferred test, significantly lower than the CI of naive males (two-sided randomization test,
in a test immediately following training or in a deferred test, significantly lower than the CI of naive males (two-sided randomization test,  );
);  -
-  in the delayed test significantly lower than in test immediately following training (two-sided randomization test,
in the delayed test significantly lower than in test immediately following training (two-sided randomization test, .
.References
-
- Swanson HI, Chan WK, Bradfield CA (1995) DNA-Binding Specificities and Pairing Rules of the Ah Receptor, Arnt, and Sim Proteins. J Biol Chem 270: 26292–26302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

