Combined use of the canine adenovirus-2 and DREADD-technology to activate specific neural pathways in vivo
- PMID: 24736748
- PMCID: PMC3988196
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095392
Combined use of the canine adenovirus-2 and DREADD-technology to activate specific neural pathways in vivo
Abstract
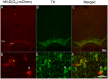
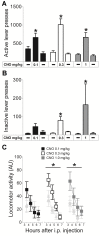
We here describe a technique to transiently activate specific neural pathways in vivo. It comprises the combined use of a CRE-recombinase expressing canine adenovirus-2 (CAV-2) and an adeno-associated virus (AAV-hSyn-DIO-hM3D(Gq)-mCherry) that contains the floxed inverted sequence of the designer receptor exclusively activated by designer drugs (DREADD) hM3D(Gq)-mCherry. CAV-2 retrogradely infects projection neurons, which allowed us to specifically express hM3D(Gq)-mCherry in neurons that project from the ventral tegmental area (VTA) to the nucleus accumbens (Acb), the majority of which were dopaminergic. Activation of hM3D(Gq)-mCherry by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of clozapine-N-oxide (CNO) leads to increases in neuronal activity, which enabled us to specifically activate VTA to Acb projection neurons. The VTA to Acb pathway is part of the mesolimbic dopamine system and has been implicated in behavioral activation and the exertion of effort. Injections of all doses of CNO led to increases in progressive ratio (PR) performance. The effect of the lowest dose of CNO was suppressed by administration of a DRD1-antagonist, suggesting that CNO-induced increases in PR-performance are at least in part mediated by DRD1-signaling. We hereby validate the combined use of CAV-2 and DREADD-technology to activate specific neural pathways and determine consequent changes in behaviorally relevant paradigms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

