The WHO Health Promoting School framework for improving the health and well-being of students and their academic achievement
- PMID: 24737131
- PMCID: PMC11214127
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008958.pub2
The WHO Health Promoting School framework for improving the health and well-being of students and their academic achievement
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization's (WHO's) Health Promoting Schools (HPS) framework is an holistic, settings-based approach to promoting health and educational attainment in school. The effectiveness of this approach has not been previously rigorously reviewed.
Objectives: To assess the effectiveness of the Health Promoting Schools (HPS) framework in improving the health and well-being of students and their academic achievement.
Search methods: We searched the following electronic databases in January 2011 and again in March and April 2013: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, CINAHL, Campbell Library, ASSIA, BiblioMap, CAB Abstracts, IBSS, Social Science Citation Index, Sociological Abstracts, TRoPHI, Global Health Database, SIGLE, Australian Education Index, British Education Index, Education Resources Information Centre, Database of Education Research, Dissertation Express, Index to Theses in Great Britain and Ireland, ClinicalTrials.gov, Current controlled trials, and WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform. We also searched relevant websites, handsearched reference lists, and used citation tracking to identify other relevant articles.
Selection criteria: We included cluster-randomised controlled trials where randomisation took place at the level of school, district or other geographical area. Participants were children and young people aged four to 18 years, attending schools or colleges. In this review, we define HPS interventions as comprising the following three elements: input to the curriculum; changes to the school's ethos or environment or both; and engagement with families or communities, or both. We compared this intervention against schools that implemented either no intervention or continued with their usual practice, or any programme that included just one or two of the above mentioned HPS elements.
Data collection and analysis: At least two review authors identified relevant trials, extracted data, and assessed risk of bias in the trials. We grouped different types of interventions according to the health topic targeted or the approach used, or both. Where data permitted, we performed random-effects meta-analyses to provide a summary of results across studies.
Main results: We included 67 eligible cluster trials, randomising 1443 schools or districts. This is made up of 1345 schools and 98 districts. The studies tackled a range of health issues: physical activity (4), nutrition (12), physical activity and nutrition combined (18), bullying (7), tobacco (5), alcohol (2), sexual health (2), violence (2), mental health (2), hand-washing (2), multiple risk behaviours (7), cycle-helmet use (1), eating disorders (1), sun protection (1), and oral health (1). The quality of evidence overall was low to moderate as determined by the GRADE approach. 'Risk of bias' assessments identified methodological limitations, including heavy reliance on self-reported data and high attrition rates for some studies. In addition, there was a lack of long-term follow-up data for most studies.We found positive effects for some interventions for: body mass index (BMI), physical activity, physical fitness, fruit and vegetable intake, tobacco use, and being bullied. Intervention effects were generally small but have the potential to produce public health benefits at the population level. We found little evidence of effectiveness for standardised body mass index (zBMI) and no evidence of effectiveness for fat intake, alcohol use, drug use, mental health, violence and bullying others; however, only a small number of studies focused on these latter outcomes. It was not possible to meta-analyse data on other health outcomes due to lack of data. Few studies provided details on adverse events or outcomes related to the interventions. In addition, few studies included any academic, attendance or school-related outcomes. We therefore cannot draw any clear conclusions as to the effectiveness of this approach for improving academic achievement.
Authors' conclusions: The results of this review provide evidence for the effectiveness of some interventions based on the HPS framework for improving certain health outcomes but not others. More well-designed research is required to establish the effectiveness of this approach for other health topics and academic achievement.
Conflict of interest statement
Rebecca Langford has undertaken consultancy work for the World Health Organization (WHO) as part of a Delphi exercise into mental health and psychosocial support in humanitarian settings.
Rona Campbell is a Director of a not‐for‐profit company, DECIPHer IMPACT Ltd, set up to enable organisations to obtain a licence to use the DECIPHer ASSIST smoking prevention programme, a peer‐led intervention for use with adolescents in secondary schools. She has made a presentation on her smoking prevention work at French Institute of Health Promotion and Health Education in Paris in April 2013 and her travel and accommodation were paid for by that organisation. Rona is married to Professor Gabriel Scally, Director of the WHO Collaborating Centre for Healthy Urban Environments. Rona has provided expert testimony to the National Institute of Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) on multiple risk behaviour on an unpaid basis. She was a member of the Wellcome Trust's Expert Group on Population and Public Health and received a small fee for attending meetings but has now stepped down from this role.
Rona’s institute has received funds for the following projects: Employer schemes to encourage walking to work: feasibility study incorporating an exploratory randomised controlled trial (NIHR Public Health Research Programme); Active For Life Year 5: a cluster‐randomised controlled trial of a primary school‐based intervention to increase levels of physical activity, decrease sedentary behaviour and improve diet (NIHR Public Health Research programme); the effectiveness, acceptability and cost effectiveness of psychosocial interventions for maltreated children and adolescents: an evidence synthesis (NIHR Health Technology Assessment programme); developing and piloting a peer mentoring intervention to reduce teenage pregnancy in looked‐after children and care leavers (NIHR Health Technology Assessment programme); adapting and piloting the ASSIST model of informal peer‐led intervention delivery to the Talk to Frank drug prevention programme in UK secondary schools (ASSIST+Frank): an exploratory trial; School Health Research Network scoping and feasibility study; the effects of Positive Youth Development interventions on substance use, violence and inequalities: systematic review of theories of change, processes and outcomes. Centre funding has also been received for NIHR School for Public Health Research and Centre for Development and Evaluation of Complex Interventions for Public Health Improvement
Elizabeth Waters and Lisa Gibbs were investigators in
Elizabeth Waters has been involved in reviews and consultancies to the WHO but not in any relation to this review.
Lisa Gibbs was also an investigator in an evaluation of the Stephanie Alexander Kitchen Garden Program.
Kelli Komro was an investigator in Project Northland (Minnesota), Project Northland (Chicago), and DARE Plus, which are included in the review. She receives royalties from the sale of the Project Northland and DARE Plus prevention curricula.
Chris Bonnell, Simon Murphy, Dan Magnus, Theodora Pouliou, Hayley Jones ‐ none known.
Figures

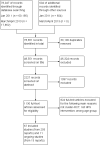
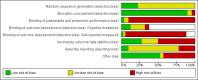


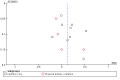


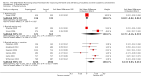
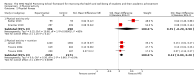

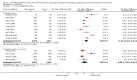



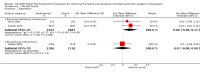

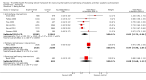
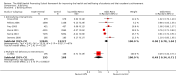
Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Anderson 2005 {published data only}
-
- Anderson AS, Porteous LEG, Foster E, Higgins C, Stead M, Hetherington M, et al. The impact of a school‐based nutrition education intervention on dietary intake and cognitive and attitudinal variables relating to fruits and vegetables. Public Health Nutrition 2005;8(6):650‐6. - PubMed
Arbeit 1992 {published data only}
-
- Arbeit ML, Johnson CC, Mott DS, Harsha DW, Nicklas TA, Webber LS, et al. The heart smart cardiovascular school health promotion: behavior correlates of risk factor change. Preventive Medicine 1992;21(1):18‐32. - PubMed
-
- Hunter SM, Johnson CC, Little‐Christian S, Nicklas TA, Harsha D, Arbeit ML, et al. Heart smart: a multifaceted cardiovascular risk reduction program for grade school students. American Journal of Health Promotion 1990;4(5):352‐60. - PubMed
Basen‐Engquist 2001 {published data only}
-
- Basen‐Engquist K, Coyle KK, Parcel GS, Kirby D, Banspach SW, Carvajal SC, et al. Schoolwide effects of a multicomponent HIV, STD, and pregnancy prevention program for high school students. Health Education & Behavior 2001;28(2):166‐85. - PubMed
-
- Basen‐Engquist K, Parcel GS, Harrist R, Kirby D, Coyle K, Banspach S, et al. The Safer Choices project: methodological issues in school‐based health promotion intervention research. Journal of School Health 1997;67(9):365‐71. - PubMed
-
- Benner TA. Safer Choices: a high‐school based program to prevent STIs, HIV, and pregnancy. In: Card JJ, Benner TA editor(s). Model Programs for Adolescent Sexual Health: Evidence‐Based HIV, STI, and Pregnancy Prevention Interventions. New York: Springer, 2008:323‐33.
-
- Coyle K, Basen‐Engquist K, Kirby D, Parcel G, Banspach S, Harrist R, et al. Short‐term impact of Safer Choices: a multicomponent, school‐based HIV, other STD, and pregnancy prevention program. Journal of School Health 1999;69(5):181‐8. - PubMed
Beets 2009 {published data only}
-
- Beets MW. Factors Associated with the Implementation Fidelity of a School‐Based Social and Character Development Program: Findings from the Positive Action Program, Hawaii [PhD thesis]. Oregon, USA: Oregon State University, 2007.
-
- Beets MW, Flay BR, Vuchinich S, Acock AC, Li KK, Allred C. School climate and teachers' beliefs and attitudes associated with implementation of the positive action program: a diffusion of innovations model. Prevention Science 2008;9(4):264‐75. - PubMed
-
- Snyder F, Flay B, Vuchinich S, Acock A, Washburn I, Beets M, et al. Impact of a social‐emotional and character development program on school‐level indicators of academic achievement, absenteeism, and disciplinary outcomes: a matched‐pair, cluster‐randomized, controlled trial. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness 2009;3(1):26‐55. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Snyder FJ. Enhancing Social‐Emotional and Character Development for Youths' Success: A Theoretical Orientation and an Evaluation using a Cluster‐Randomized Design [PhD thesis]. Oregon, USA: Oregon State University, 2012.
Bere 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bere E, Veierød MB, Bjelland M, Klepp K‐I. Free school fruit—sustained effect 1 year later. Health Education Research 2006;21(2):268‐75. - PubMed
-
- Bere E, Veierød MB, Bjelland M, Klepp K‐I. Outcome and process evaluation of a Norwegian school‐randomized fruit and vegetable intervention: Fruits and Vegetables Make the Marks (FVMM). Health Education Research 2006;21(2):258‐67. - PubMed
Bond 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bond L, Glover S, Godfrey C, Butler H, Patton GC. Building capacity for system‐level change in schools: lessons from the Gatehouse Project. Health Education & Behavior 2001;28(3):368‐83. - PubMed
-
- Bond L, Thomas L, Coffey C, Glover S, Butler H, Carlin JB, et al. Long‐term Impact of the Gatehouse Project on cannabis use of 16‐year‐olds in Australia. Journal of School Health 2004;74(1):23‐9. - PubMed
-
- Patton G, Bond L, Butler H, Glover S. Changing schools, changing health? Design and implementation of the Gatehouse Project. Journal of Adolescent Health 2003;33(4):231‐9. - PubMed
Bowen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bowen A, Ma H, Ou J, Billhimer W, Long T, Mintz E, et al. A cluster‐randomized controlled trial evaluating the effect of a handwashing‐promotion program in Chinese primary schools. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2007;76(6):1166‐73. - PubMed
Brandstetter 2012 {published data only}
-
- Brandstetter S, Klenk J, Berg S, Galm C, Fritz M, Peter R, et al. Overweight prevention implemented by primary school teachers: a randomised controlled trial. Obesity Facts 2012; Vol. 5, issue 1:1‐11. - PubMed
-
- Kesztyüs D, Schreiber A, Wirt T, Wiedom M, Dreyhaupt J, Brandstetter S, et al. Economic evaluation of URMEL‐ICE, a school‐based overweight prevention programme comprising metabolism, exercise and lifestyle intervention in children. European Journal of Health Economics 2013; Vol. 14, issue 2:185‐95. - PubMed
-
- Nagel G, Wabitsch M, Galm C, Berg S, Brandstetter S, Fritz M, et al. Determinants of obesity in the Ulm Research on Metabolism, Exercise and Lifestyle in Children (URMEL‐ICE). European Journal of Pediatrics 2009;168(10):1259‐67. - PubMed
Caballero 2003 {published data only}
-
- Caballero B. Introduction: obesity prevention in American Indian schoolchildren: the Pathways study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1999; Vol. 69, issue 4 Suppl:745‐6s.
-
- Cunningham‐Sabo L, Snyder MP, Anliker J, Thompson J, Weber JL, Thomas O, et al. Impact of the Pathways food service intervention on breakfast served in American‐Indian schools. Preventive Medicine 2003;37(6 Pt 2):S46‐54. - PubMed
Colín‐Ramírez 2010 {published data only}
-
- Colín‐Ramírez E, Castillo‐Martinez L, Orea‐Tejeda A, Vergara A, Villa AR. Impact of a school‐based intervention for cardiovascular risk factors prevention (RESCATE) on physical activity and diet in Mexican children aged 8‐10 years [Efecto de una intervención escolar basada enactividad física y dieta para la prevención defactores de riesgo cardiovascular (RESCATE)en niños mexicanos de 8 a 10 años]. Revista Española de Nutrición Comunitaria 2009;15(2):71‐80.
-
- Colín‐Ramírez E, Castillo‐Martinez L, Orea‐Tejeda A, Vergara‐Castaneda A, Keirns‐Davis C, Villa‐Romero A. Outcomes of a school‐based intervention (RESCATE) to improve physical activity patterns in Mexican children aged 8‐10 years. Health Education Research 2010;25(6):1042‐9. - PubMed
Crespo 2012 {published data only}
Cross 2011 {published data only}
-
- Cross D, Monks H, Hall M, Shaw T, Pintabona Y, Erceg E, et al. Three‐year results of the Friendly Schools whole‐of‐school intervention on children's bullying behaviour. British Educational Research Journal 2011;37(1):105‐29.
-
- Cross D, Pintabona Y, Hall M, Hamilton G, Erceg E. Validated guidelines for school‐based bullying prevention and management. International Journal of Mental Health Promotion 2004;6(3):34‐42.
-
- Cross D, Pintabona Y, Hall M, Hamilton G, Erceg E, Roberts C. The Friendly Schools Project: an empirically grounded school‐based bullying prevention program. Australian Journal of Guidance and Counselling 2003;13(1):36‐46.
Cross 2012 {published data only}
-
- Cross D, Waters S, Pearce N, Shaw T, Hall M, Erceg E, et al. The Friendly Schools Friendly Families Programme: three‐year bullying behaviour outcomes in primary school children. International Journal of Educational Research 2012;53:394‐406.
De Vries (Denmark) 2003 {published data only}
-
- Vries H, Dijk F, Wetzels J, Mudde A, Kremers S, Ariza C, et al. The European Smoking Prevention Framework Approach (ESFA): effects after 24 and 30 months. Health Education Research 2006;21(1):116‐32. - PubMed
-
- Vries H, Mudde A, Kremers S, Wetzels J, Uiters E, Ariza C, et al. The European Smoking Prevention Framework Approach (ESFA): short‐term effects. Health Education Research 2003;18(6):649‐63. - PubMed
-
- Vries H, Mudde A, Leijs I, Charlton A, Vartiainen E, Buijs G, et al. The European Smoking Prevention Framework Approach (EFSA): an example of integral prevention. Health Education Research 2003;18(5):611‐26. - PubMed
-
- Holm K, Kremers S, Vries H. Why do Danish adolescents take up smoking?. European Journal of Public Health 2003;13(1):67‐74. - PubMed
De Vries (Finland) 2003 {published data only}
-
- Vries H, Dijk F, Wetzels J, Mudde A, Kremers S, Ariza C, et al. The European Smoking Prevention Framework Approach (ESFA): effects after 24 and 30 months. Health Education Research 2006;21(1):116‐32. - PubMed
-
- Vries H, Mudde A, Kremers S, Wetzels J, Uiters E, Ariza C, et al. The European Smoking Prevention Framework Approach (ESFA): short‐term effects. Health Education Research 2003;18(6):649‐63. - PubMed
-
- Vries H, Mudde A, Leijs I, Charlton A, Vartiainen E, Buijs G, et al. The European Smoking Prevention Framework Approach (EFSA): an example of integral prevention. Health Education Research 2003;18(5):611‐26. - PubMed
-
- Vartiainen E, Pennanen M, Haukkala A, Dijk F, Lehtovuori R, Vries H. The effects of a three‐year smoking prevention programme in secondary schools in Helsinki. European Journal of Public Health 2007;17(3):249‐56. - PubMed
Eather 2013 {published data only}
-
- Eather N, Morgan P, Lubans D. Improving the fitness and physical activity levels of primary school children: results of the Fit‐4‐Fun group randomized controlled trial. Preventive Medicine 2013;56(1):12‐9. - PubMed
Eddy 2003 {published data only}
-
- Eddy JM, Reid JB, Fetrow RA. An elementary school‐based prevention program targeting modifiable antecedents of youth delinquency and violence: Linking the Interests of Families and Teachers (LIFT). Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders 2000;8(3):165‐76.
-
- Eddy JM, Reid JB, Stoolmiller M, Fetrow RA. Outcomes during middle school for an elementary school‐based preventive intervention for conduct problems: follow‐up results from a randomized trial. Behavior Therapy 2003;34(4):535‐52.
-
- Reid JB, Eddy JM, Fetrow RA, Stoolmiller M. Description and immediate impacts of a preventive intervention for conduct problems. American Journal of Community Psychology 1999;27(4):483‐517. - PubMed
Evans 2013 {published data only}
-
- Christian MS, Evans CEL, Ransley JK, Greenwood DC, Thomas JD, Cade JE. Process evaluation of a cluster randomised controlled trial of a school‐based fruit and vegetable intervention: Project Tomato. Public Health Nutrition 2012;15(3):459‐65. - PubMed
-
- Ransley J, Taylor E, Radwan Y, Kitchen M, Greenwood D, Cade J. Does nutrition education in primary schools make a difference to children’s fruit and vegetable consumption?. Public Health Nutrition 2010;13(11):1898‐904. - PubMed
Fekkes 2006 {published data only}
-
- Fekkes M, Pijpers FI, Verloove‐Vanhorick SP. Effects of antibullying school program on bullying and health complaints. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2006;160(6):638‐44. - PubMed
Flay 2004 {published data only}
-
- Fagen MC, Flay BR. Sustaining a school‐based prevention program: results from the Aban Aya Sustainability Project. Health Education & Behavior 2009;36(1):9‐23. - PubMed
Foster 2008 {published data only}
-
- Foster GD, Sherman S, Borradaile KE, Grundy KM, Vander Veur SS, Nachmani J, et al. A policy‐based school intervention to prevent overweight and obesity. Pediatrics 2008;121(4):e794‐802. - PubMed
-
- Rappaport EB, Daskalakis C, Sendecki JA. Using routinely collected growth data to assess a school‐based obesity prevention strategy. International Journal of Obesity 2013;37(1):79‐85. - PubMed
Foster 2010 {published data only}
Frey 2005 {published data only}
-
- Brown EC, Low S, Smith BH, Haggerty KP. Outcomes from a school‐randomized controlled trial of steps to respect: a bullying prevention program. School Psychology Review 2011;40(3):423‐33.
-
- Frey KS, Hirschstein MK, Edstrom LV, Snell JL. Observed reductions in school bullying, nonbullying aggression, and destructive bystander behavior: a longitudinal evaluation. Journal of Educational Psychology 2009;101(2):466‐81.
-
- Frey KS, Hirschstein MK, Snell JL, Schoiack Edstrom L, Mackenzie EP, Broderick CJ. Reducing playground bullying and supporting beliefs: an experimental trial of the Steps to Respect program. Developmental Psychology 2005;41(3):479‐90. - PubMed
-
- Hirschstein M, Frey KS. Promoting behavior and beliefs that reduce bullying: the Steps to Respect Program. In: Jimerson S, Furlong M editor(s). The Handbook of School Violence and School Safety: From Research to Practice. Erlbaum Associates, Inc, 2006.
Grydeland 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bergh IH, Bjelland M, Grydeland M, Lien N, Andersen LF, Klepp K‐I, et al. Mid‐way and post‐intervention effects on potential determinants of physical activity and sedentary behavior, results of the HEIA study ‐ a multi‐component school‐based randomized trial. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2012;9(1):63. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bergh IH, Grydeland M, Bjelland M, Lien N, Andersen LF, Klepp K‐I, et al. Personal and social‐environmental correlates of objectively measured physical activity in Norwegian pre‐adolescent children. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports 2011;21(6):e315‐24. - PubMed
-
- Bjelland M, Bergh IH, Grydeland M, Klepp K‐I, Andersen LF, Anderssen SA, et al. Changes in adolescents’ intake of sugar‐sweetened beverages and sedentary behaviour: results at 8 month mid‐way assessment of the HEIA study ‐ a comprehensive, multi‐component school‐based randomized trial. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2011;8:63. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bjelland M, Lien N, Bergh IH, Grydeland M, Anderssen SA, Klepp K‐I, et al. Overweight and waist circumference among Norwegian 11‐year‐olds and associations with reported parental overweight and waist circumference: the HEIA study. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health 2010;38(5 Suppl):19‐27. - PubMed
Haerens 2006 {published data only}
-
- Haerens L, Cerin E, Maes L, Cardon G, Deforche B, Bourdeaudhuij I. Explaining the effect of a 1‐year intervention promoting physical activity in middle schools: a mediation analysis. Public Health Nutrition 2008;11(5):501‐12. - PubMed
-
- Haerens L, Bourdeaudhuij I, Maes L, Cardon G, Deforche B. School‐based randomized controlled trial of a physical activity intervention among adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health 2007;40(3):258‐65. - PubMed
-
- Haerens L, Bourdeaudhuij I, Maes L, Vereecken C, Brug J, Deforche B. The effects of a middle‐school healthy eating intervention on adolescents' fat and fruit intake and soft drinks consumption. Public Health Nutrition 2007;10(5):443‐9. - PubMed
-
- Haerens L, Deforche B, Maes L, Cardon G, Stevens V, Bourdeaudhuij I. Evaluation of a 2‐year physical activity and healthy eating intervention in middle school children. Health Education Research 2006;21(6):911‐21. - PubMed
Hall 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hall M, Cross D, Howat P, Stevenson M, Shaw T. Evaluation of a school‐based peer leader bicycle helmet intervention. Injury Control and Safety Promotion 2004;11(3):165‐74. - PubMed
Hamilton 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hamilton G, Cross D, Resnicow K, Hall M. A school‐based harm minimization smoking intervention trial: outcome results. Addiction 2005;100(5):689‐700. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton G, Cross D, Resnicow K, Shaw T. Does harm minimisation lead to greater experimentation? Results from a school smoking intervention trial. Drug and Alcohol Review 2007;26(6):605‐13. - PubMed
Hoffman 2010 {published data only}
Hoppu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hoppu U, Lehtisalo J, Kujala J, Keso T, Garam S, Tapanainen H, et al. The diet of adolescents can be improved by school intervention. Public Health Nutrition 2010;13(6A):973‐9. - PubMed
-
- Hoppu U, Lehtisalo J, Tapanainen H, Pietinen P. Dietary habits and nutrient intake of Finnish adolescents. Public Health Nutrition 2010;13(6A):965–72. - PubMed
Jansen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Jansen W, Borsboom G, Meima A, Zwanenburg EJ, Mackenbach JP, Raat H, et al. Effectiveness of a primary school‐based intervention to reduce overweight. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2011;6(2‐2):e70‐7. - PubMed
Kärnä 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ahtola A, Haataja A, Kärnä A, Poskiparta E, Salmivalli C. For children only? Effects of the KiVa antibullying program on teachers. Teaching and Teacher Education 2012;28(6):851‐9.
-
- Kärnä A, Voeten M, Little TD, Poskiparta E, Kaljonen A, Salmivalli C. A large‐scale evaluation of the KiVa antibullying program: grades 4‐6. Child Development 2011;82(1):311‐30. - PubMed
-
- Salmivalli C, Poskiparta E. KiVa antibullying program: overview of evaluation studies based on a randomized controlled trial and national rollout in Finland. International Journal of Conflict and Violence 2012;6(2):294‐301.
-
- Salmivalli C, Poskiparta E. Making bullying prevention a priority in Finnish schools: the KiVa antibullying program. New Directions for Youth Development 2012;133:41‐53. - PubMed
-
- Williford A, Boulton A, Noland B, Little TD, Kärnä A, Salmivalli C. Effects of the KiVa anti‐bullying program on adolescents' depression, anxiety, and perception of peers. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 2012;40(2):289‐300. - PubMed
Kärnä 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ahtola A, Haataja A, Kärnä A, Poskiparta E, Salmivalli C. For children only? Effects of the KiVa antibullying program on teachers. Teaching and Teacher Education 2012;28(6):851‐9.
-
- Kärnä A, Voeten M, Little TD, Alanen E, Poskiparta E, Salmivalli C. Effectiveness of the KiVa antibullying program: grades 1‐3 and 7‐9. Journal of Educational Psychology 2013;105(2):535‐51.
-
- Salmivalli C, Poskiparta E. KiVa antibullying program: overview of evaluation studies based on a randomized controlled trial and national rollout in Finland. International Journal of Conflict and Violence 2012;6(2):294‐301.
-
- Salmivalli C, Poskiparta E. Making bullying prevention a priority in Finnish schools: the KiVa antibullying program. New Directions for Youth Development 2012;2012(133):41‐53. - PubMed
Komro 2008 {published data only}
-
- Komro KA, Perry CL, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Bosma LM, Dudovitz BS, Williams CL, et al. Brief report: the adaptation of Project Northland for urban youth. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2004;29(6):457‐66. - PubMed
Kriemler 2010 {published data only}
-
- Zahner L, Puder JJ, Roth R, Schmid M, Guldimann R, Puhse U, et al. A school‐based physical activity program to improve health and fitness in children aged 6‐13 years ("Kinder‐Sportstudie KISS"): study design of a randomized controlled trial [ISRCTN15360785]. BMC Public Health 2006;6:147. - PMC - PubMed
Levy 2012 {published data only}
Li 2011 {published data only}
-
- Li KK, Washburn I, DuBois D, Vuchinich S, Ji P, Brechling V, et al. Effects of the Positive Action programme on problem behaviours in elementary school students: a matched‐pair randomised control trial in Chicago. Psychology and Health 2011;26(2):187–204. - PubMed
-
- Washburn I, Acock A, Vuchinich S, Snyder F, Li K, Ji P, et al. Effects of a social‐emotional and character development program on the trajectory of behaviors associated with social‐emotional and character development: findings from three randomized trials. Prevention Science 2011;12(3):314‐23. - PubMed
Llargues 2011 {published data only}
Luepker 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Edmundson EW, Luton SC, McGraw SA, Kelder SH, Layman AK, Smyth MH, et al. Catch ‐ classroom process evaluation in a multicenter trial. Health Education Quarterly 1994;Suppl 2:S27‐50. - PubMed
-
- Elder JP, McGraw SA, Stone EJ, Reed DB, Harsha DW, Greene T, et al. CATCH: process evaluation of environmental factors and programs. Health Education Quarterly 1994;Suppl 2:S107‐27. - PubMed
-
- Heath EM, Coleman KJ. Adoption and institutionalization of the Child and Adolescent Trial for Cardiovascular Health (CATCH) in El Paso, Texas. Health Promotion Practice 2003;4(2):157‐64. - PubMed
-
- Heath EM, Coleman KJ. Evaluation of the institutionalization of the coordinated approach to child health (CATCH) in a U.S/Mexico border community. Health Education & Behavior 2002;29(4):444‐60. - PubMed
-
- Hoelscher DM, Feldman HA, Johnson CC, Lytle LA, Osganian SK, Parcel GS, et al. School‐based health education programs can be maintained over time: results from the CATCH Institutionalization study. Preventive Medicine 2004;38(5):594‐606. - PubMed
Lytle 2004 {published data only}
-
- Birnbaum AS, Lytle LA, Story M, Perry CL, Murray DM. Are differences in exposure to a multicomponent school‐based intervention associated with varying dietary outcomes in adolescents?. Health Education & Behavior 2002;29(4):427‐43. - PubMed
-
- Janega JB, Murray DM, Varnell SP, Blitstein JL, Birnbaum AS, Lytle LA. Assessing intervention effects in a school‐based nutrition intervention trial: which analytic model is most powerful?. Health Education & Behavior 2004;31(6):756‐74. - PubMed
-
- Lytle LA, Kubik MY, Perry C, Story M, Birnbaum AS, Murray DM. Influencing healthful food choices in school and home environments: results from the TEENS study. Preventive Medicine 2006;43(1):8‐13. - PubMed
-
- Lytle LA, Murray DM, Perry CL, Story M, Birnbaum AS, Kubik MY, et al. School‐based approaches to affect adolescents' diets: results from the TEENS study. Health Education & Behavior 2004;31(2):270‐87. - PubMed
McVey 2004 {published data only}
-
- McVey G, Tweed S, Blackmore E. Healthy Schools‐Healthy Kids: a controlled evaluation of a comprehensive universal eating disorder prevention program. Body Image 2007;4(2):115‐36. - PubMed
Nicklas 1998 {published data only}
-
- Beech BM, Rice R, Myers L, Johnson C, Nicklas TA. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices related to fruit and vegetable consumption of high school students. Journal of Adolescent Health 1999;24(4):244‐50. - PubMed
-
- Nicklas TA, Johnson CC, Farris R, Rice R, Lyon L, Shi R. Development of a school‐based nutrition intervention for high school students: Gimme 5. American Journal of Health Promotion 1997;11(5):315‐22. - PubMed
-
- Nicklas TA, Johnson CC, Myers L, Farris RP, Cunningham A. Outcomes of a high school program to increase fruit and vegetable consumption: Gimme 5 ‐ a fresh nutrition concept for students. Journal of School Health 1998;68(6):248‐53. - PubMed
-
- Nicklas TA, O’Neil CE. Process of conducting a 5‐a‐day intervention with high school students: Gimme 5 (Louisiana). Health Education & Behavior 2000;27(2):201‐12. - PubMed
-
- O'Neil C, Nicklas T. Gimme 5: an innovative school‐based nutrition intervention for high school students. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 2002;102(3 Suppl):S93‐6. - PubMed
Olson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Olson AL, Gaffney C, Starr P, Gibson JJ, Cole BF, Dietrich AJ. SunSafe in the middle school years: a community‐wide intervention to change early‐adolescent sun protection. Pediatrics 2007;119(1):e247‐56. - PubMed
Orpinas 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kelder SH, Orpinas P, McAlister A, Frankowski R, Parcel GS, Friday J. The students for peace project: a comprehensive violence‐prevention program for middle school students. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 1996;12(5 Suppl):22‐30. - PubMed
-
- Orpinas P, Kelder S, Frankowski R, Murray N, Zhang Q, McAlister A. Outcome evaluation of a multi‐component violence‐prevention program for middle schools: the Students for Peace project. Health Education Research 2000;15(1):45‐58. - PubMed
Perry 1996 {published data only}
-
- Komro KA, Perry CL, Murray DM, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Williams CL, Anstine PS. Peer‐planned social activities for preventing alcohol use among young adolescents. Journal of School Health 1996;66(9):328‐34. - PubMed
-
- Komro KA, Perry CL, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Williams CL. Peer participation in Project Northland: a community‐wide alcohol use prevention project. Journal of School Health 1994;64(8):318‐22. - PubMed
-
- Komro KA, Perry CL, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Williams CL, Roel JP. Peer leadership in school and community alcohol use prevention activities. Journal of Health Education 1999;30(4):202‐8.
-
- Komro KA, Perry CL, Williams CL, Stigler MH, Farbakhsh K, Veblen‐Mortenson S. How did Project Northland reduce alcohol use among young adolescents? Analysis of mediating variables. Health Education Research 2001;16(1):59‐70. - PubMed
-
- Perry CL, Lee S, Stigler MH, Farbakhsh K, Komro KA, Gewirtz AH, et al. The impact of Project Northland on selected MMPI‐A problem behavior scales. Journal of Primary Prevention 2007;28(5):449‐65. - PubMed
Perry 1998 {published data only}
-
- Eldridge AL, Smith‐Warner SA, Lytle LA, Murray DM. Comparison of 3 methods for counting fruits and vegetables for fourth‐grade students in the Minnesota 5 A Day Power Plus Program. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 1998;98(7):777‐82. - PubMed
-
- Story M, Mays RW, Bishop DB, Perry CL, Taylor G, Smyth M, et al. 5‐a‐Day Power Plus: process evaluation of a multicomponent elementary school program to increase fruit and vegetable consumption. Health Education & Behavior 2000;27(2):187‐200. - PubMed
Perry 2003 {published data only}
-
- Eischens A, Komro KA, Perry CL, Bosma LM, Farbakhsh K. The association of extracurricular activity participation with substance use among youth in the DARE Plus project. American Journal of Health Education 2004;35(2):68‐75.
-
- Komro K, Perry C, Munson K, Stigler M, Farbakhsh K. Reliability and validity of self‐report measures to evaluate drug and violence prevention programs. Journal of Child & Adolescent Substance Abuse 2004;13(3):17‐51.
-
- Komro KA, Perry CL, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Stigler MH, Bosma LM, Munson KA, et al. Violence‐related outcomes of the D.A.R.E. plus project. Health Education & Behavior 2004;31(3):335‐54. - PubMed
-
- Perry CL, Komro KA, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Bosma L, Munson K, Stigler M, et al. The Minnesota DARE PLUS Project: creating community partnerships to prevent drug use and violence. Journal of School Health 2000;70(3):84‐8. - PubMed
-
- Perry CL, Komro KA, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Bosma LM, Farbakhsh K, Munson KA, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the middle and junior high school D.A.R.E and D.A.R.E Plus programs. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2003;157(2):178‐84. - PubMed
Perry 2009 {published data only}
-
- Mathur C, Stigler MH, Perry CL, Arora A, Reddy KS. Differences in prevalence of tobacco use among Indian urban youth: the role of socioeconomic status. Nicotine & Tobacco Research 2008;10(1):109–16. - PubMed
-
- Mishra A, Arora M, Stigler MH, Komro KA, Lytle LA, Reddy KS, et al. Indian youth speak about tobacco: results of focus group discussions with school students. Health Education & Behavior 2005;32(2):363‐79. - PubMed
Radcliffe 2005 {published data only}
-
- Radcliffe B, Ogden C, Welsh J, Carroll S, Coyne T, Craig P. The Queensland School Breakfast Project: a health promoting schools approach. Nutrition & Dietetics 2005;62(1):33‐40.
Reynolds 2000 {published data only}
-
- Harrington K, Binkley D, Reynolds K, Duvall R, Copeland J, Franklin F, et al. Recruitment issues in school‐based research: lessons learned from the High 5 Alabama Project. Journal of School Health 1997;67(10):415‐21. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds KD, Franklin FA, Binkley D, Raczynski JM, Harrington KF, Kirk KA, et al. Increasing the fruit and vegetable consumption of fourth‐graders: results from the High 5 Project. Preventive Medicine 2000;30(4):309‐19. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds KD, Franklin FA, Leviton LC, Maloy J, Harrington KF, Yaroch AL, et al. Methods, results, and lessons learned from process evaluation of the high 5 school‐based nutrition intervention. Health Education & Behavior 2000;27(2):177‐86. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds KD, Raczynski JM, Binkley D, Franklin FA, Duvall RC, Devane‐Hart K, et al. Design of "High 5": a school‐based study to promote fruit and vegetable consumption for reduction of cancer risk. Journal of Cancer Education 1998;13(3):169‐77. - PubMed
Ross 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hayes RJ, Changalucha J, Ross DA, Gavyole A, Todd J, Obasi AIN, et al. The MEMA kwa Vijana Project: design of a community randomised trial of an innovative adolescent sexual health intervention in rural Tanzania. Contemporary Clinical Trials 2005;26(4):430‐42. - PubMed
-
- Larke N, Cleophas‐Mazige B, Plummer ML, Obasi AIN, Rwakatare M, Todd J, et al. Impact of the MEMA kwa Vijana adolescent sexual and reproductive health interventions on use of health services by young people in rural Mwanza, Tanzania: results of a cluster randomized trial. Journal of Adolescent Health 2010;47(5):512‐22. - PubMed
-
- Obasi A, Cleophas B, Ross D, Chima K, Mmassy G, Gavyole A, et al. Rationale and design of the MEMA kwa Vijana adolescent sexual and reproductive health intervention in Mwanza Region, Tanzania. AIDS Care 2006;18(4):311‐22. - PubMed
-
- Plummer ML, Wight D, Obasi AIN, Wamoyi J, Mshana G, Todd J, et al. A process evaluation of a school‐based adolescent sexual health intervention in rural Tanzania: the MEMA kwa Vijana programme. Health Education Research 2007;22(4):500‐12. - PubMed
Rush 2012 {published data only}
-
- Graham D, Appleton S, Rush E, McLennan S, Reed P, Simmons D. Increasing activity and improving nutrition through a schools‐based programme: Project Energize. 1. Design, programme, randomisation and evaluation methodology. Public Health Nutrition 2008;11(10):1076‐84. - PubMed
-
- Rush E, Reed P, McLennan S, Coppinger T, Simmons D, Graham D. A school‐based obesity control programme: Project Energize. Two‐year outcomes. British Journal of Nutrition 2012;107(4):581‐7. - PubMed
Sahota 2001 {published data only}
Sallis 2003 {published data only}
-
- Sallis JF, McKenzie TL, Conway TL, Elder JP, Prochaska JJ, Brown M, et al. Environmental interventions for eating and physical activity: a randomized controlled trial in middle schools. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2003;24(3):209‐17. - PubMed
Sawyer 2010 {published data only}
-
- Burns J, Hickie I. Depression in young people: a national school‐based initiative for prevention, early intervention and pathways for care. Australasian Psychiatry 2002;10(2):134‐8.
-
- Sawyer MG, Harchak TF, Spence SH, Bond L, Graetz B, Kay D, et al. School‐based prevention of depression: a 2‐year follow‐up of a randomized controlled trial of the beyondblue schools research initiative. Journal of Adolescent Health 2010;47(3):297‐304. - PubMed
-
- Sawyer MG, Pfeiffer S, Spence SH, Bond L, Graetz B, Kay D, et al. School‐based prevention of depression: a randomised controlled study of the beyondblue schools research initiative. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 2010;51(2):199‐209. - PubMed
-
- Spence S, Burns J, Boucher S, Glover S, Graetz B, Kay D, et al. The beyondblue Schools Research Initiative: conceptual framework and intervention. Australasian Psychiatry 2005;13(2):159‐64. - PubMed
Schofield 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lynagh M, Knight J, Schofield MJ, Paras L. Lessons learned from the Hunter Region Health Promoting Schools Project in New South Wales, Australia. Journal of School Health 1999;69(6):227‐32. - PubMed
-
- Schofield MJ, Lynagh M, Mishra G. Evaluation of a Health Promoting Schools program to reduce smoking in Australian secondary schools. Health Education Research 2003;18(6):678‐92. - PubMed
Simon 2006 {published data only}
-
- Simon C, Schweitzer B, Drai J, Kellou N, Sandalinas F, Reitzer C, et al. Overweight prevention in adolescents by increasing physical activity: 6‐year results of the randomized ICAPS study. Obesity Reviews 2011;12:26.
-
- Simon C, Schweitzer B, Oujaa M, Wagner A, Arveiler D, Triby E, et al. Successful overweight prevention in adolescents by increasing physical activity: a 4‐year randomized controlled intervention. International Journal of Obesity 2008;32(10):1489‐98. - PubMed
-
- Simon C, Wagner A, DiVita C, Rauscher E, Klein‐Platat C, Arveiler D, et al. Intervention centred on adolescents' physical activity and sedentary behaviour (ICAPS): concept and 6‐month results. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders 2004;28 Suppl 3:S96‐103. - PubMed
-
- Simon C, Wagner A, Platat C, Arveiler D, Schweitzer B, Schlienger JL, et al. ICAPS: a multilevel program to improve physical activity in adolescents. Diabetes & Metabolism 2006;32(1):41‐9. - PubMed
Simons‐Morton 2005 {published data only}
-
- Simons‐Morton B, Chen R, Abroms L, Haynie DL. Latent growth curve analyses of peer and parent influences on smoking progression among early adolescents. Health Psychology 2004;23(6):612‐21. - PubMed
-
- Simons‐Morton B, Haynie D, Saylor K, Crump AD, Chen R. The effects of the going places program on early adolescent substance use and antisocial behavior. Prevention Science 2005;6(3):187‐97. - PubMed
-
- Simons‐Morton B, Haynie D, Saylor K, Crump Aria D, Chen R. Impact analysis and mediation of outcomes: the Going Places program. Health Education & Behavior 2005;32(2):227‐41. - PubMed
Stevens 2000 {published data only}
-
- Stevens V, Bourdeaudhuij I, Oost P. Bullying in Flemish schools: an evaluation of anti‐bullying intervention in primary and secondary schools. British Journal of Educational Psychology 2000;70:195‐210. - PubMed
-
- Stevens V, Oost P, Bourdeaudhuij I. The effects of an anti‐bullying intervention programme on peers' attitudes and behaviour. Journal of Adolescence 2000;23:21‐34. - PubMed
Tai 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tai BJ, Jiang H, Du MQ, Peng B. Assessing the effectiveness of a school‐based oral health promotion programme in Yichang City, China. Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology 2009;37(5):391‐8. - PubMed
Talaat 2011 {published data only}
Te Velde 2008 {published data only}
-
- Brug J, Yngve A, Kleep K‐I. The pro children study: conceptualization, baseline results and intervention development of a European effort to promote fruit and vegetable consumption in schoolchildren. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism 2005;49(4):209‐11. - PubMed
-
- Klepp K‐I, Perez‐Rodrigo C, Bourdeaudhuij I, Due PP, Elmadfa I, Haraldsdottir J, et al. Promoting fruit and vegetable consumption among European schoolchildren: rationale, conceptualization and design of the pro children project. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism 2005;49(4):212‐20. - PubMed
-
- Klepp K‐I, Rodrigo CP, Thorsdottir I, Due P, Vaz de Almeida MD, Elmadfa I, et al. Promoting and sustaining health through increased vegetable and fruit consumption among European schoolchildren: the Pro Children Project. Journal of Public Health 2005;13(2):97‐101.
-
- Rodrigo P, Aranceta J, Brug H, Wind M, Hildonen C, Klepp K‐I. School‐based education strategies to promote fruit and vegetable consumption: the Pro Children Project. Archivos Latinoamericanos de Nutrición 2004;54:14‐9. - PubMed
-
- Velde SJ, Brug J, Wind M, Hildonen C, Bjelland M, Pérez‐Rodrigo C, et al. Effects of a comprehensive fruit‐ and vegetable‐promoting school‐based intervention in three European countries: the Pro Children Study. British Journal of Nutrition 2008;99(4):893‐903. - PubMed
Trevino 2004 {published data only}
-
- Trevino RP, Yin Z, Hernandez A, Hale DE, Garcia OA, Mobley C. Impact of the Bienestar school‐based diabetes mellitus prevention program on fasting capillary glucose levels: a randomized controlled trial. [Erratum appears in Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2005;159(4):341]. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2004;158(9):911‐7. - PMC - PubMed
Trevino 2005 {published data only}
-
- Trevino RP, Hernandez AE, Yin Z, Garcia OA, Hernandez I. Effect of the Bienestar health program on physical fitness in low‐income Mexican American children. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences 2005;27:120‐32.
-
- Trevino RP, Marshall RM, Hernandez AE, Ramirez G. Bienestar: a diabetes risk factor modification program. Diabetes 1999;48:A305.
-
- Trevino RP, Pugh JA, Hernandez AE, Menchaca VD, Ramirez RR, Mendoza M. Bienestar: a diabetes risk‐factor prevention program. Journal of School Health 1998;68(2):62‐7. - PubMed
Wen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Fry D, Wen LM, Merom D, Dirkis H, Rissel C, Balafas A. The Central Sydney Walk to School Research Program 2005‐2007. Sydney: NSW Department of Health, 2009.
-
- Wen LM, Fry D, Merom D, Rissel C, Dirkis H, Balafas A. Increasing active travel to school: are we on the right track? A cluster randomised controlled trial from Sydney, Australia. Preventive Medicine 2008;47(6):612‐8. - PubMed
Wen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Wen XZ, Chen WQ, Lu CY, Liang CH, Zhang CX, Han K, et al. Process evaluation on a health promotion model regarding smoking prevention among Chinese secondary school students. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2007;28(3):224‐8. - PubMed
Williamson 2012 {published data only}
Wolfe 2009 {published data only}
-
- Wolfe DA, Crooks C, Jaffe P, Chiodo D, Hughes R, Ellis W, et al. A school‐based program to prevent adolescent dating violence: a cluster randomized trial. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2009;163(8):692‐9. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe DA, Crooks CV, Chiodo D, Hughes R, Ellis W. Observations of adolescent peer resistance skills following a classroom‐based healthy relationship program: a post‐intervention comparison. Prevention Science 2012;13(2):196‐205. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Al‐Sheyab 2012 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Sheyab N, Gallagher R, Crisp J, Shah S. Peer‐led education for adolescents with asthma in Jordan: a cluster‐randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics 2012;129(1):e106‐12. - PubMed
Baranowski 2000 {published data only}
-
- Baranowski T, Davis M, Resnicow K, Baranowski J, Doyle C, Lin LS, et al. Gimme 5 fruit, juice, and vegetables for fun and health: outcome evaluation. Health Education & Behavior 2000;27(1):96‐111. - PubMed
-
- Davis M, Baranowski T, Resnicow K, Baranowski J, Doyle C, Smith M, et al. Gimme 5 fruit and vegetables for fun and health: process evaluation. Health Education & Behavior 2000;27(2):167‐76. - PubMed
Bessems 2011 {published data only}
Bierman 1999 {published data only}
Bierman 2010 {published data only}
Braswell 1997 {published data only}
-
- Braswell L, August G, Bloomquist M, Realmuto G, Skare SS, Crosby RD. School‐based secondary prevention for children with disruptive behavior: initial outcomes. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology 1997;25(3):197‐208. - PubMed
Christian 2012 {published data only}
Clark 2004 {published data only}
-
- Clark N, Brown R, Joseph C, Anderson E, Liu M, Valerio M. Effects of a comprehensive school‐based asthma program on symptoms, parent management, grades, and absenteeism. Chest 2004;125(5):1674‐9. - PubMed
Clark 2010 {published data only}
Coleman 2012 {published data only}
-
- Coleman KJ, Shordon M, Caparosa SL, Pomichowski ME, Dzewaltowski DA. The healthy options for nutrition environments in schools (Healthy ONES) group randomized trial: using implementation models to change nutrition policy and environments in low income schools. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2012;9:80. - PMC - PubMed
Collard 2010 {published data only}
-
- Collard DC, Chinapaw MJ, Mechelen W, Verhagen EA. Design of the iPlay study: systematic development of a physical activity injury prevention programme for primary school children. Sports Medicine 2009;39(11):889‐901. - PubMed
-
- Collard DC, Verhagen EA, Chinapaw MJ, Knol DL, Mechelen W. Effectiveness of a school‐based physical activity injury prevention program: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine 2010;164(2):145‐50. - PubMed
De Coen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Coen V, Bourdeaudhuij I, Vereecken C, Verbestel V, Haerens, Huybrechts I, et al. Effects of a 2‐year healthy eating and physical activity intervention for 3–6‐year‐olds in communities of high and low socio‐economic status: the POP (Prevention of Overweight among Pre‐school and school children) project. Public Health Nutrition 2012; Vol. 15, issue 9:1737‐45. - PubMed
De Silva‐Sanigorski 2010 {published data only}
Dietrich 1998 {published data only}
-
- Dietrich AJ, Olson AL, Sox CH, Stevens M, Tosteson TD, Ahles T, et al. A community‐based randomized trial encouraging sun protection for children. Pediatrics 1998;102(6):e64. - PubMed
-
- Dietrich AJ, Olson AL, Sox CH, Tosteson TD, Grant‐Petersson J. Persistent increase in children's sun protection in a randomized controlled community trial. Preventive Medicine 2000;31(5):569‐74. - PubMed
-
- Grant‐Petersson J, Dietrich AJ, Sox CH, Winchell CW, Stevens MM. Promoting sun protection in elementary schools and child care settings: the SunSafe Project. Journal of School Health 1999;69(3):100‐6. - PubMed
Gingiss 2006 {published data only}
-
- Boerm M, Gingiss PM, Roberts‐Gray C. Association of the presence of state and district health education policies with school tobacco prevention program practices. Journal of School Health 2007;77(4):207‐14. - PubMed
-
- Gingiss P, Boerm M, Roberts‐Gray C. Follow‐up comparisons of intervention and comparison schools in a state tobacco prevention and control initiative. Journal of School Health 2006; Vol. 76, issue 3:98‐103. - PubMed
-
- Gingiss PM, Boerm M. Influence of funding cuts on Texas school tobacco programs. Journal of School Health 2009;79(8):361‐8. - PubMed
-
- Gingiss PM, Roberts‐Gray C, Boerm M. Bridge‐it: a system for predicting implementation fidelity for school‐based tobacco prevention programs. Prevention Science 2006;7(2):197‐207. - PubMed
-
- Roberts‐Gray C, Gingiss PM, Boerm M. Evaluating school capacity to implement new programs. Evaluation and Program Planning 2007;30(3):247‐57. - PubMed
Graf 2011 {published data only}
-
- Graf C, Dordel S. The CHILT I project (Children's Health Interventional Trial): a multicomponent intervention to prevent physical inactivity and overweight in primary schools [Das CHILT‐I‐projekt (Children's Health InterventionaL Trial): eine multimodale manahme zur pravention von bewegungsmangel und ubergewicht an grundschulen]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt, Gesundheitsforschung, Gesundheitsschutz 2011;54(3):313‐21. - PubMed
Haggerty 2006 {published data only}
-
- Catalano RF, Mazza JJ, Harachi TW, Abbott RD, Haggerty KP, Fleming CB. Raising healthy children through enhancing social development in elementary school: results after 1.5 years. Journal of School Psychology 2003;41(2):143‐64.
-
- Fleming CB, Harachi TW, Catalano RF, Haggerty KP, Abbott RD. Assessing the effects of a school‐based intervention on unscheduled school transfers during elementary school. Evaluation Review 2001;25(6):655‐79. - PubMed
-
- Haggerty KP, Fleming CB, Catalano RF, Harachi TW, Abbott RD. Raising Healthy Children: examining the impact of promoting healthy driving behavior within a social development intervention. Prevention Science 2006;7(3):257‐67. - PubMed
Horne 2009 {published data only}
-
- Horne PJ, Hardman CA, Lowe CF, Tapper K, Noury J, Madden P, et al. Increasing parental provision and children's consumption of lunchbox fruit and vegetables in Ireland: the Food Dudes intervention. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2009;63(5):613‐8. - PubMed
Hunter 2010 {published data only}
Irwin 2012 {published data only}
-
- Irwin C, Irwin R, Richey P, Miller M, Boddie J, Dickerson T. Get fit with the Grizzlies: a community‐school‐home initiative to fight childhood obesity led by a professional sports organization. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics 2012;172:163‐7. - PubMed
James 1998 {published data only}
-
- James EL. A Strategy to Improve School Based Health Promotion: A Case Study in Smoking Prevention [PhD thesis]. Callaghan, New South Wales, Australia: University of Newcastle, 1998.
-
- James EL, Heller RF. A randomised controlled trial of school smoking prevention programs: using epidemiological methods to evaluate health promotion [abstract]. Australasian Epidemiology 1999;6:19‐20.
Jiang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Jiang J, Xia X, Greiner T, Wu G, Lian G, Rosenqvist U. The effects of a 3‐year obesity intervention in schoolchildren in Beijing. Child: Care, Health and Development 2007;33(5):641‐6. - PubMed
Johnson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Johnson CC, Myers L, Webber LS, Boris NW, He H, Brewer D. A school‐based environmental intervention to reduce smoking among high school students: the Acadiana Coalition of Teens against Tobacco (ACTT). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2009;6(4):1298‐316. - PMC - PubMed
Johnston 2013 {published data only}
-
- Johnston CA, Moreno JP, El‐Mubasher A, Gallagher M, Tyler C, Woehle D. Impact of a school‐based pediatric obesity prevention program facilitated by health professionals. Journal of School Health 2013;83(3):171‐81. - PubMed
LoScuito 1988 {published data only}
-
- LoSciuto L, Ausetts MA. Evaluation of a drug abuse prevention program: a field experiment. Addictive Behaviors 1988;13(4):337‐51. - PubMed
Lubans 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lubans DR, Morgan PJ, Callister R, Collins CE. Effects of integrating pedometers, parental materials, and E‐mail support within an extracurricular school sport intervention. Journal of Adolescent Health 2009;44(2):176‐83. - PubMed
Lubans 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lubans DR, Morgan PJ, Weaver K, Callister R, Dewar DL, Costigan SA, et al. Rationale and study protocol for the supporting children's outcomes using rewards, exercise and skills (SCORES) group randomized controlled trial: a physical activity and fundamental movement skills intervention for primary schools in low‐income communities. BMC Public Health 2012;12:427. - PMC - PubMed
Magnusson 2012 {published data only}
-
- Magnusson KT, Hrafnkelsson H, Sigurgeirsson I, Johannsson E, Sveinsson T. Limited effects of a 2‐year school‐based physical activity intervention on body composition and cardiorespiratory fitness in 7‐year‐old children. Health Education Research 2012;27(3):484‐94. - PubMed
Nagamatsu 2011 {published data only}
Naylor 2008 {published data only}
-
- Macdonald HM, Kontulainen SA, Khan KM, McKay HA. Is a school‐based physical activity intervention effective for increasing tibial bone strength in boys and girls?. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 2007;22(3):434‐46. - PubMed
-
- Macdonald HM, Kontulainen SA, Petit MA, Beck TJ, Khan KM, McKay HA. Does a novel school‐based physical activity model benefit femoral neck bone strength in pre‐ and early pubertal children?. Osteoporosis International 2008;19(10):1445‐56. - PubMed
-
- Naylor P, Scott J, Drummond J, Bridgewater L, McKay HA, Panagiotopoulos C. Implementing a whole school physical activity and healthy eating model in rural and remote first nations schools: a process evaluation of Action Schools! BC. Rural and Remote Health 2010;10(2):1296. - PubMed
-
- Naylor PJ, Macdonald HM, Warburton DER, Reed KE, McKay HA. An active school model to promote physical activity in elementary schools: Action Schools! BC. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2008;42(5):338‐43. - PubMed
Neumark‐Sztainer 2003 {published data only}
-
- Neumark‐Sztainer D, Story M, Hannan J, Rex J. New Moves: a school‐based obesity prevention program for adolescent girls. Preventive Medicine 2003;37(1):41‐51. - PubMed
Pate 2005 {published data only}
-
- Dishman RK, Motl RW, Saunders R, Felton G, Ward DS, Dowda M, et al. Enjoyment mediates effects of a school‐based physical‐activity intervention. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2005;37(3):478‐87. - PubMed
-
- Dishman RK, Motl RW, Saunders R, Felton G, Ward DS, Dowda M, et al. Self‐efficacy partially mediates the effect of a school‐based physical‐activity intervention among adolescent girls. Preventive Medicine 2004;38(5):628–36. - PubMed
-
- Saunders RP, Ward D, Felton GM, Dowda M, Pate RR. Examining the link between program implementation and behavior outcomes in the lifestyle education for activity program (LEAP). Evaluation and Program Planning 2006;29(4):352–64. - PubMed
Piper 2000 {published data only}
-
- Moberg DP, Piper DL. The Healthy for Life project: sexual risk behavior outcomes. AIDS Education and Prevention 1998;10(2):128‐48. - PubMed
-
- Piper DL, Moberg DP, King MJ. The Healthy for Life project: behavioral outcomes. Journal of Primary Prevention 2000;21(1):47‐73.
Prinz 2000 {published data only}
-
- Dumas JE, Lynch AM, Laughlin JE, Phillips Smith, Prinz RJ. Promoting intervention fidelity. Conceptual issues, methods, and preliminary results from the EARLY ALLIANCE prevention trial. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2001;20(1 Suppl):38‐47. - PubMed
-
- Dumas JE, Prinz RJ, Smith EP, Laughlin J. The EARLY ALLIANCE prevention trial: an integrated set of interventions to promote competence and reduce risk for conduct disorder, substance abuse, and school failure. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review 1999;2(1):37‐53. - PubMed
-
- Prinz RJ, Dumas JE, Smith EP, Laughlin JE. The EARLY ALLIANCE prevention trial: a dual design to test reduction of risk for conduct problems, substance abuse, and school failure in childhood. Controlled Clinical Trials 2000;21(3):286‐302. - PubMed
Reddy 2002 {published data only}
-
- Reddy KS, Arora M, Perry CL, Nair B, Kohli A, Lytle LA, et al. Tobacco and alcohol use outcomes of a school‐based intervention in New Delhi. American Journal of Health Behavior 2002;26(3):173‐81. - PubMed
Sevinç 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sevinç Ö, Bozkurt A, Gündoğdu M, Baş Aslan U, Ağbuğa B, Aslan S, et al. Evaluation of the effectiveness of an intervention program on preventing childhood obesity in Denizli, Turkey. Turkish Journal of Medical Science 2011; Vol. 41, issue 6:1097‐105.
Simon 2008 {published data only}
Singhal 2010 {published data only}
-
- Singhal N, Misra A, Shah P, Gulati S. Effects of controlled school‐based multi‐component model of nutrition and lifestyle interventions on behavior modification, anthropometry and metabolic risk profile of urban Asian Indian adolescents in North India. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2010; Vol. 64, issue 4:364‐73. - PubMed
Solomon 1988 {published data only}
-
- Battistich V. Effects of a program to enhance prosocial development on adjustment. Paper presented at the 98th Annual Meeting of the American Psychological Association; 1990 August 10‐14; Boston (MA). 1990.
-
- Battistich V. Effects of a school‐based program to enhance prosocial development on children's peer relations and social adjustment. Journal of Research in Character Education 2003;1:1‐16.
-
- Battistich V, Solomon D, Watson M, Solomon J, Schaps E. Effects of an elementary school program to enhance prosocial behavior on children's cognitive‐social problem‐solving skills and strategies. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology 1989;10(2):147‐69.
-
- Solomon D, Watson M, Delucchi K, Schaps E, Battistich V. Enhancing children's prosocial behavior in the classroom. American Educational Research Journal 1988; Vol. 25, issue 4:527‐54.
Wang 2006a {published data only}
-
- Wang Y, Tussing L, Odoms‐Young A, Braunschweig C, Flay B, Hedeker D, et al. Obesity prevention in low socioeconomic status urban African‐American adolescents: study design and preliminary findings of the HEALTH‐KIDS Study. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2006;60(1):92‐103. - PubMed
Washburn (southeastern state) 2011 {published data only}
-
- Washburn I, Acock A, Vuchinich S, Snyder F, Li K, Ji P, et al. Effects of a social‐emotional and character development program on the trajectory of behaviors associated with social‐emotional and character development: findings from three randomized trials. Prevention Science 2011; Vol. 12, issue 3:314‐23. - PubMed
Webber 2008 {published data only}
Webster‐Stratton 2008 {published data only}
-
- Webster‐Stratton C, Herman KC. Disseminating Incredible Years series early‐intervention programs: integrating and sustaining services between school and home. Psychology in the Schools 2010;47(1):36‐54.
-
- Webster‐Stratton C, Herman KC. The impact of parent behavior‐management training on child depressive symptoms. Journal of Counseling Psychology 2008;55(4):473‐84. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Dreyhaupt 2012 {published data only}
Hodder 2012 {published data only}
-
- Hodder R, Freund M, Bowman J, Wolfenden L, Campbell E, Wye P, et al. A cluster randomised trial of a school‐based resilience intervention to decrease tobacco, alcohol and illicit drug use in secondary school students: study protocol. BMC Public Health 2012;12:1009. [ACTRN12611000606987] - PMC - PubMed
Malmberg 2010 {published data only}
NCT00747513 {published data only}
-
- Lerner‐Geva L. A multi‐component program to reduce obesity in children. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00747513 (accessed 5 March 2014). [NCT00747513]
Salmon 2011 {published data only}
-
- Carson V, Salmon J, Arundell L, Ridgers N, Cerin E, Brown H, et al. Examination of mid‐intervention mediating effects on objectively assessed sedentary time among children in the Transform‐Us! cluster‐randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2013;10:62. - PMC - PubMed
Siegrist 2011 {published data only}
Sutherland 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sutherland R, Campbell E, Lubans D, Morgan P, Okely A, Nathan N, et al. A cluster randomised trial of a school‐based intervention to prevent decline in adolescent physical activity levels: study protocol for the 'Physical Activity 4 Everyone' trial. BMC Public Health 2013;13:57. [ACTRN12612000382875] - PMC - PubMed
Wang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Wang Y, Tussing L, Odoms‐Young A, Braunschweig C, Flay B, Hedeker D, et al. Obesity prevention in low socioeconomic status urban African‐American adolescents: study design and preliminary findings of the HEALTH‐KIDS study. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2006; Vol. 60, issue 1:92‐103. - PubMed
Waters 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gibbs L, O'Connor T, Waters E, Booth M, Walsh O, Green J, et al. Addressing the potential adverse effects of school‐based BMI assessments on children's wellbeing. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2008;3(1):52‐7. - PubMed
-
- Waters E, Ashbolt R, Gibbs L, Booth M, Magarey A, Gold L, et al. Double disadvantage: the influence of ethnicity over socioeconomic position on childhood overweight and obesity: findings from an inner urban population of primary school children. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2008;3(4):196‐204. [ACTRN12607000385448] - PubMed
Wyatt 2013 {published data only}
Xu 2012 {published data only}
-
- Xu F, Ware RS, Tse LA, Wang Z, Hong X, Song A, et al. A school‐based comprehensive lifestyle intervention among Chinese kids against obesity (CLICK‐Obesity): rationale, design and methodology of a randomized controlled trial in Nanjing city, China. BMC Public Health 2012;12:316. [ChiCTR‐ERC‐11001819] - PMC - PubMed
Additional references
Allison 2007
Angold 1995
-
- Angold A, Costello EJ, Messer SC, Pickles A, Winder F, Silver D, et al. Development of a short questionnaire for use in epidemiological studies of depression in children and adolescents. International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research 1995;5:237‐49.
Berkman 2002
-
- Berkman DS, Lescano AG, Gilman RH, Lopez SL, Black MM. Effects of stunting, diarrhoeal disease, and parasitic infection during infancy on cognition in late childhood: a follow‐up study. Lancet 2002;359(9306):564‐71. - PubMed
Bonell 2012
-
- Bonell C, Fletcher A, Morton M, Lorenc T, Moore L. Realist randomised controlled trials: a new approach to evaluating complex public health interventions. Social Science & Medicine 2012;75(12):2299‐306. - PubMed
Bonell 2013
-
- Bonell C, Parry W, Wells H, Jamal F, Fletcher A, Harden A, et al. The effects of the school environment on student health: a systematic review of multi‐level studies. Health & Place 2013;21:180‐91. - PubMed
Borenstein 2009
-
- Borenstein M, Hedges L, Higgins J, Rothstein H. Introduction to Meta‐Analysis. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 2009.
Bowers 2004
-
- Bowers T. Stress, teaching and teacher health. Education 3‐13 2004;32(3):73‐80.
Brown 2009
-
- Brown T, Summerbell C. Systematic review of school‐based interventions that focus on changing dietary intake and physical activity levels to prevent childhood obesity: an update to the obesity guidance produced by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Obesity Reviews 2009;10(1):110‐41. - PubMed
Campbell 2004
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks J, Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Denman 1999
-
- Denman S. Health promoting schools in England ‐ a way forward in development. Journal of Public Health Medicine 1999;21(2):215‐20. - PubMed
Deschesnes 2003
-
- Deschesnes M, Martin C, Hill A. Comprehensive approaches to school health promotion: how to achieve broader implementation?. Health Promotion International 2003;18(4):387‐96. - PubMed
Dobbins 2013
Faggiano 2005
Farrington 2009
Felitti 1998
-
- Felitti VJ, Anda RF, Nordenberg D, Williamson DF, Spitz AM, Edwards V, et al. Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults. the Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) study. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 1998;14(4):245‐58. - PubMed
Foxcroft 2011
Galobardes 2006
-
- Galobardes B, Smith GD, Lynch JW. Systematic review of the influence of childhood socioeconomic circumstances on risk for cardiovascular disease in adulthood. Annals of Epidemiology 2006;16(2):91‐104. - PubMed
Ganann 2010
-
- Ganann R, Fitzpatrick‐Lewis D, Ciliska D, Dobbins M, Krishnaratne S, Beyers J, et al. Community‐based interventions for enhancing access to or consumption of fruit and vegetables (or both) among five to 18‐year olds. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue 8. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008644] - DOI
Grantham‐McGregor 1995
-
- Grantham‐McGregor S. A review of studies of the effect of severe malnutrition on mental development. Journal of Nutrition 1995;125(8 Suppl):s2233‐8. - PubMed
Green 2011
-
- Green S, Higgins J, Alderson P, Clarke M, Mulrow C, Oxman A. Introduction. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Grieve 2012
-
- Grieve R. Chapter 9: Other topics. A Practical Guide to Cluster Randomised Trials in Health Services Research. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 2012.
Hawe 2004
Health Education Boards 1996
-
- Health Education Board for Scotland, Health Promotion Wales, Health Education Authority (England), Health Promotion Agency for Northern Ireland. The European Network of Health Promoting Schools: introduction ‐ the UK project. Health Education Journal 1996;55(4):447‐9.
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. Chicester: John Wiley & Sons.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks J, Altman D. Part 3: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated march 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons.
Howerton 2007
-
- Howerton MW, Bell BS, Dodd KW, Berrigan D, Stolzenberg‐Solomon R, Nebeling L. School‐based nutrition programs produced a moderate increase in fruit and vegetable consumption: meta and pooling analyses from 7 Studies. Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior 2007;39(4):186‐96. - PubMed
Hurrelman 2006
-
- Hurrelman K, Richter M. Risk behaviours in adolescence: the relationship between developmental and health problems. Journal of Public Health 2006;14(1):20‐8.
IUHPE 2008
-
- International Union for Health Promotion and Education. Achieving health promoting schools: guidelines for promoting health in schools. Version 2 of the document formerly known as "Protocols and guidelines for health promoting schools". www.iuhpe.org/images/PUBLICATIONS/THEMATIC/HPS/HPSGuidelines_ENG.pdf (accessed 6 February 2014).
IUHPE 2010
-
- International Union for Health Promotion and Education. Promoting health in schools: from evidence to action. www.dhhs.tas.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0007/117385/PHiSFromEvidenceT... (accessed 13 March 2013).
Jackson 2005
-
- Jackson N, Waters E, for the Guidelines for Systematic Reviews in Health Promotion and Public Health Taskforce. Criteria for the systematic review of health promotion and public health interventions. Health Promotion International 2005;20(4):367‐74. - PubMed
Kavanagh 2008
-
- Kavanagh J, Oliver S, Lorenc T. Reflections on developing and using PROGRESS‐Plus. Equity Update 2008; Vol. 2, issue 1:1‐3.
Kelder 1994
Kessler 2010
Kidger 2012
-
- Kidger J, Araya R, Donovan J, Gunnell D. The effect of the school environment on the emotional health of adolescents: a systematic review. Pediatrics 2012;129(5):925‐49. - PubMed
Kroesbergen 1996
-
- Kroesbergen HT, Wit CA, Stijnen TH. Detection of depressive complaints in children. European Journal of Public Health 1996;6(1):29‐34.
Lang 2013
-
- Lang IA, Marlow R, Goodman R, Meltzer H, Ford T. Influence of problematic child‐teacher relationships on future psychiatric disorder: population survey with 3‐year follow‐up. British Journal of Psychiatry 2013;202(5):336‐41. - PubMed
Langford 2011
Lister‐Sharp 1999
-
- Lister‐Sharp D, Chapman S, Stewart‐Brown S, Sowden A. Health promoting schools and health promotion in schools: two systematic reviews. Health Technology Assessments 1999;3(22):1‐209. - PubMed
Lynagh 1997
-
- Lynagh M, Schofield J, Sanson‐Fisher R. School health promotion programmes over the past decade: a review of the smoking, alcohol and solar protection literature. Health Promotion International 1997;12(1):43‐60.
Lyons 2009
Lyons 2012
-
- Lyons RA, Hutchings H, Rodgers SE, Hyatt MA, Demmler J, Gabbe BJ, et al. Development and use of a privacy‐protecting total population record linkage system to support observational, interventional, and policy relevant research. Lancet 2012;380:s6.
MacIntyre 2003
-
- MacIntyre S. Evaluating the evidence on measures to reduce inequalities in health. In: Oliver A, Exworthy M editor(s). Health Inequalities: Evidence, Policy and Implementation. Proceedings from a Meeting of the Health Equity Network. London: The Nuffield Trust, 2003:e23‐8.
Marshall 2000
-
- Marshall BJ, Sheehan MM, Northfield JR, Maher S, Carlisle R, Leger L. School‐based health promotion across Australia. Journal of School Health 2000;70:251‐2. - PubMed
MRC 2000
-
- Medical Research Council. A framework for development and evaluation of RCTs for complex interventions to improve health. www.mrc.ac.uk/Utilities/Documentrecord/index.htm?d=MRC003372 (accessed 6 February 2014).
Mytton 2006
Mũkoma 2004
-
- Mũkoma W, Flisher A. Evaluations of health promoting schools: a review of nine studies. Health Promotion International 2004;19(3):357‐68. - PubMed
Nader 2008
-
- Nader PR, Bradley RH, Houts RM, McRitchie SL, O'Brien M. Moderate‐to‐vigorous physical activity from ages 9 to 15 years. JAMA 2008;300(3):295‐305. - PubMed
Nutbeam 1992
-
- Nutbeam D. The health promoting school: closing the gap between theory and practice. Health Promotion International 1992;7(3):151‐3.
Nutbeam 1998
-
- Nutbeam D. Evaluating health promotion ‐ progress, problems and solutions. Health Promotion International 1998;13(1):27‐44.
Parsons 1996
-
- Parsons C, Stears D, Thomas C. The health promoting school in Europe: conceptualising and evaluating the change. Health Education Journal 1996;55(3):311‐21.
Perry 2002
-
- Perry CL, Williams CL, Komro KA, Veblen‐Mortenson S, Stigler MH, Munson KA, et al. Project Northland: long‐term outcomes of community action to reduce adolescent alcohol use. Health Education Research 2002;17(1):117‐32. - PubMed
Poulton 2002
Powney 2000
-
- Powney J, Malcolm H, Lowden K. Health and Attainment: A Brief Review of Recent Literature. The Scottish Council for Research in Education, 2000.
Radloff 1977
-
- Radloff LS. The CES‐D scale: a self‐report depression scale for research in the general population. Applied Psychological Measurement 1977;1(3):385–401.
Rogers 1998
-
- Rogers E, Moon AM, Mullee MA, Speller VM, Roderick PJ. Developing the 'health‐promoting school' ‐ a national survey of healthy schools awards. Public Health 1998;112(1):37‐40. - PubMed
Rose 1985
-
- Rose G. Sick individuals and sick populations. International Journal of Epidemiology 1985;14(1):32‐8. - PubMed
Rychetnik 2002
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann H, Oxman A, Vist G, Higgins J, Deeks J Glasziou P, Guyatt G. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Shepperd 2009
Singh 2008
-
- Singh AS, Mulder C, Twisk JWR, Mechelen W, Chinapaw MJM. Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature. Obesity Reviews 2008;9(5):474‐88. - PubMed
St Leger 1998
-
- Leger L. Australian teachers' understandings of the health promoting school concept and the implications for the development of school health. Health Promotion International 1998;13(3):223‐35.
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta‐analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011;343:d4002. - PubMed
Stewart‐Brown 2006
-
- Stewart‐Brown S. What is the evidence on school health promotion in improving or preventing disease and, specifically, what is the effectiveness of the health promoting schools approach?. www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0007/74653/E88185.pdf (accessed 4 March 2014).
Suhrcke 2011
-
- Suhrcke M, Paz Nieves C. The impact of health and health behaviours on educational outcomes in high‐income countries: a review of the evidence. www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0004/134671/e94805.pdf (accessed 30 March 2014).
Thomas 2013
Tones 2000
-
- Tones K. Evaluating health promotion: a tale of three errors. Patient Education and Counseling 2000;39(2‐3):227‐36. - PubMed
Wadsworth 1997
-
- Wadsworth M, Kuh D. Childhood influences on adult health: a review of recent work from the British 1946 national birth cohort study, the MRC national survey of health and development. Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology 1997;11(1):2‐20. - PubMed
Waters 2011
Whitaker 1997
-
- Whitaker RC, Wright JA, Pepe MS, Seidel KD, Dietz WH. Predicting obesity in young adulthood from childhood and parental obesity. New England Journal of Medicine 1997;337(13):869‐73. - PubMed
White 2005
-
- White IR, Thomas J. Standardized mean differences in individually‐randomized and cluster‐randomized trials, with applications to meta‐analysis. Clinical Trials 2005;2(2):141‐51. - PubMed
WHO 1986
-
- World Health Organization. Ottowa Charter for Health Promotion. Copenhagen: Regional Office for Europe, 1986.
WHO 1997
-
- World Health Organization. Promoting health through schools. Report of a WHO Expert Committee on comprehensive school health education and promotion. WHO technical report series 870. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/trs/WHO_TRS_870.pdf (accessed 30 March 2014). - PubMed
WHO 1998
-
- World Health Organization. Health‐promoting schools: a healthy setting for living, learning and working. www.who.int/school_youth_health/media/en/92.pdf (accessed 30 March 2014).
WHO 1999
-
- World Health Organization Europe. Health promotion evaluation: Recommendations for policy makers. Copenhagen: WHO Working group on Health Promotion Evaluation, 1999.
World Education Forum 2008
-
- World Education Forum. Focusing resources on effective school health: a FRESH start to enhancing the quality and equity of education. Final Report, 2008. www.unicef.org/lifeskills/files/FreshDocument.pdf (accessed 21 November 2013).
Wright 2001
Young 1989
-
- Young I, Williams T. The Healthy School. Edinburgh: Scottish Health Education Group, 1989.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

