Fetal alcohol syndrome surveillance: age of syndrome manifestation in case ascertainment
- PMID: 24737611
- PMCID: PMC4169739
- DOI: 10.1002/bdra.23245
Fetal alcohol syndrome surveillance: age of syndrome manifestation in case ascertainment
Abstract
Background: Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is a leading cause of developmental disability (Abel & Sokol, ). Active public health surveillance through medical record abstraction has been used to estimate FAS prevalence rates, typically based on birth cohorts. There is an extended time for FAS characteristics to become apparent in infants and young children, and there are often delays in syndrome recognition and documentation. This methodological study analyzes the age at case ascertainment in a large surveillance program.
Methods: The Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Surveillance (FASSLink) Project, funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, sought to estimate FAS prevalence rates in eight U.S. states. FASSLink used linked abstractions from multiple health care records of suspected cases of FAS. The present study analyzed data from this effort to determine the child's age in months at confirming abstraction.
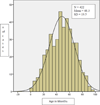
Results: The average age at abstraction for confirmed/probable FAS cases (n = 422) was 48.3 (±19.5) months with a range of 0 to 94 months. Age of ascertainment varied by state and decreased with each birth year; the number of cases ascertained also decreased in a steep stepwise gradient over the 6 birth years in the study.
Conclusion: FAS surveillance efforts should screen records of children who are much older than is typical in birth defects surveillance. To best establish rates of FAS using medical records abstraction, surveillance efforts should focus on 1-year birth cohorts followed for a fixed number of years or, if using multi-year cohorts, should implement staggered end dates allowing all births to be followed for up to 8 years of age.
Keywords: age at ascertainment; fetal alcohol syndrome; record abstraction; surveillance.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methods for surveillance of fetal alcohol syndrome: The Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Surveillance Network II (FASSNetII) - Arizona, Colorado, New York, 2009 - 2014.Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2015 Mar;103(3):196-202. doi: 10.1002/bdra.23335. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2015. PMID: 25761572 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and behaviors of mothers who have a child with fetal alcohol syndrome.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2012 Jan-Feb;34(1):90-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2011.09.010. Epub 2011 Oct 7. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2012. PMID: 22001355
-
Prevalence and characteristics of fetal alcohol syndrome and partial fetal alcohol syndrome in a Rocky Mountain Region City.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015 Oct 1;155:118-27. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.08.006. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015. PMID: 26321671 Free PMC article.
-
Counting fetal alcohol spectrum disorder in Australia: the evidence and the challenges.Drug Alcohol Rev. 2013 Sep;32(5):461-7. doi: 10.1111/dar.12047. Epub 2013 Apr 25. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23617437 Review.
-
Estimating the prevalence of fetal alcohol syndrome. A summary.Alcohol Res Health. 2001;25(3):159-67. Alcohol Res Health. 2001. PMID: 11810953 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prenatal maternal alcohol exposure: diagnosis and prevention of fetal alcohol syndrome.Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2022 Sep;65(5):385-394. doi: 10.5468/ogs.22123. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35908651 Free PMC article.
-
Why are Birth Defects Surveillance Programs Important?Front Public Health. 2021 Nov 2;9:753342. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.753342. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34796160 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Forty Years of Assessing Neurodevelopmental and Behavioral Effects of Prenatal Alcohol Exposure in Infants: What Have We Learned?Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019 Aug;43(8):1632-1642. doi: 10.1111/acer.14127. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019. PMID: 31206743 Free PMC article.
-
Administratively reported fetal alcohol spectrum disorders in commercially- and Medicaid-insured samples of children in the United States, 2015 - 2021.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2024 Oct 1;263:112420. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2024.112420. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2024. PMID: 39208694
References
-
- Abel EL, Sokol RJ. Fetal alcohol syndrome is now leading cause of mental retardation. Lancet. 1986;328(8517):1222. - PubMed
-
- Abel EL, Martier S, Durger M, Ager J, Sokol RJ. Ratings of fetal alcohol syndrome facial features by medical providers and biomedical scientists. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 1993;17:717–721. - PubMed
-
- Burd L, Martsolf JT. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome: Diagnosis and syndromal variability. Physiology and Behavior. 1989;46:39–43. - PubMed
-
- Burd L, Shin M, Dixon-Gray L, Elliott A, Fershteyn Z, Moberg DP, O’Leary L, Ruttenber M FASSLink Team. Population based surveillance for fetal alcohol syndrome in infants and young children. 2011 Unpublished manuscript.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous