Molecular pathways: interleukin-15 signaling in health and in cancer
- PMID: 24737791
- PMCID: PMC3989546
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3603
Molecular pathways: interleukin-15 signaling in health and in cancer
Abstract
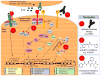
Interleukin-15 (IL-15) is a proinflammatory cytokine involved in the development, survival, proliferation, and activation of multiple lymphocyte lineages utilizing a variety of signaling pathways. IL-15 utilizes three distinct receptor chains in at least two different combinations to signal and exert its effects on the immune system. The binding of IL-15 to its receptor complex activates an "immune-enhancing" signaling cascade in natural killer cells and subsets of T cells, as well as the induction of a number of proto-oncogenes. Additional studies have explored the role of IL-15 in the development and progression of cancer, notably leukemia of large granular lymphocytes, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. This review provides an overview of the molecular events in the IL-15 signaling pathway and the aberrancies in its regulation that are associated with chronic inflammation and cancer. We briefly explore the potential therapeutic opportunities that have arisen as a result of these studies to further the treatment of cancer. These involve both targeting the disruption of IL-15 signaling as well as IL-15-mediated enhancement of innate and antigen-specific immunity.
©2014 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Armitage RJ, Macduff BM, Eisenman J, Paxton R, Grabstein KH. IL-15 has stimulatory activity for the induction of B cell proliferation and differentiation. J Immunol. 1995;154:483–90. - PubMed
-
- Mrozek E, Anderson P, Caligiuri MA. Role of interleukin-15 in the development of human CD56+ natural killer cells from CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood. 1996;87:2632–40. - PubMed
-
- Cooper MA, Bush JE, Fehniger TA, VanDeusen JB, Waite RE, Liu Y, et al. In vivo evidence for a dependence on interleukin 15 for survival of natural killer cells. Blood. 2002;100:3633–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

