Genes for regeneration
- PMID: 24737866
- PMCID: PMC3985189
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.02517
Genes for regeneration
Abstract
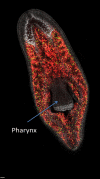
FoxA, an evolutionarily conserved gene involved in the development of the digestive system in many animals, has an important role in regeneration in flatworms.
Keywords: pharynx; planaria; regeneration; single-organ regeneration; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment on
-
Selective amputation of the pharynx identifies a FoxA-dependent regeneration program in planaria.Elife. 2014 Apr 15;3:e02238. doi: 10.7554/eLife.02238. Elife. 2014. PMID: 24737865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ang SL, Wierda A, Wong D, Stevens KA, Cascio S, Rossant J, Zaret KS. 1993. The formation and maintenance of the definitive endoderm lineage in the mouse: involvement of HNF3/forkhead proteins. Development 119:1301–1315 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

